The mammalian Excretory System
Kidney Structure and the Nephron Scott Gilbert, MD

Kidney Atlas and Diseases Robert W. Schrier
Normal Vascular and Glomerular Structure, RW. Schrier



A – corpuscolo renale B – tubulo prossimale C – tubulo contorto distale D – juxtaglomerulare 1. Membrana basale 2. Capsula di Bowman - parietale 3. Capsula di Bowman - viscerale 3a. Pedicelli (podociti) 3b. Podociti 4. spazio di Bowman (spazio delle vie urinarie) 5a. Mesangium - cellule Intraglomerulari 5b. Mesangium – cellule extraglomerulari 6. Cellule granulari (cellule juxtaglomerulari) 7. Macula densa 8. Miociti (muscolatura liscia) 9. Arteriola afferente 10. Glomerulo Capillari 11. Arteriola efferente

Vascularization

From Wikipedia
Primary Disorders of Phosphate Metabolism
 Renal Physiology, Utah 2001
Renal Physiology, Utah 2001
Kidney physiology


Kidney transport

Probenecid and anion transport

big gamma-L-glutamyl-L-DOPA inhibits Na+-phosphate cotransport across renal brush border membranes and increases renal excretion of phosphate 1998
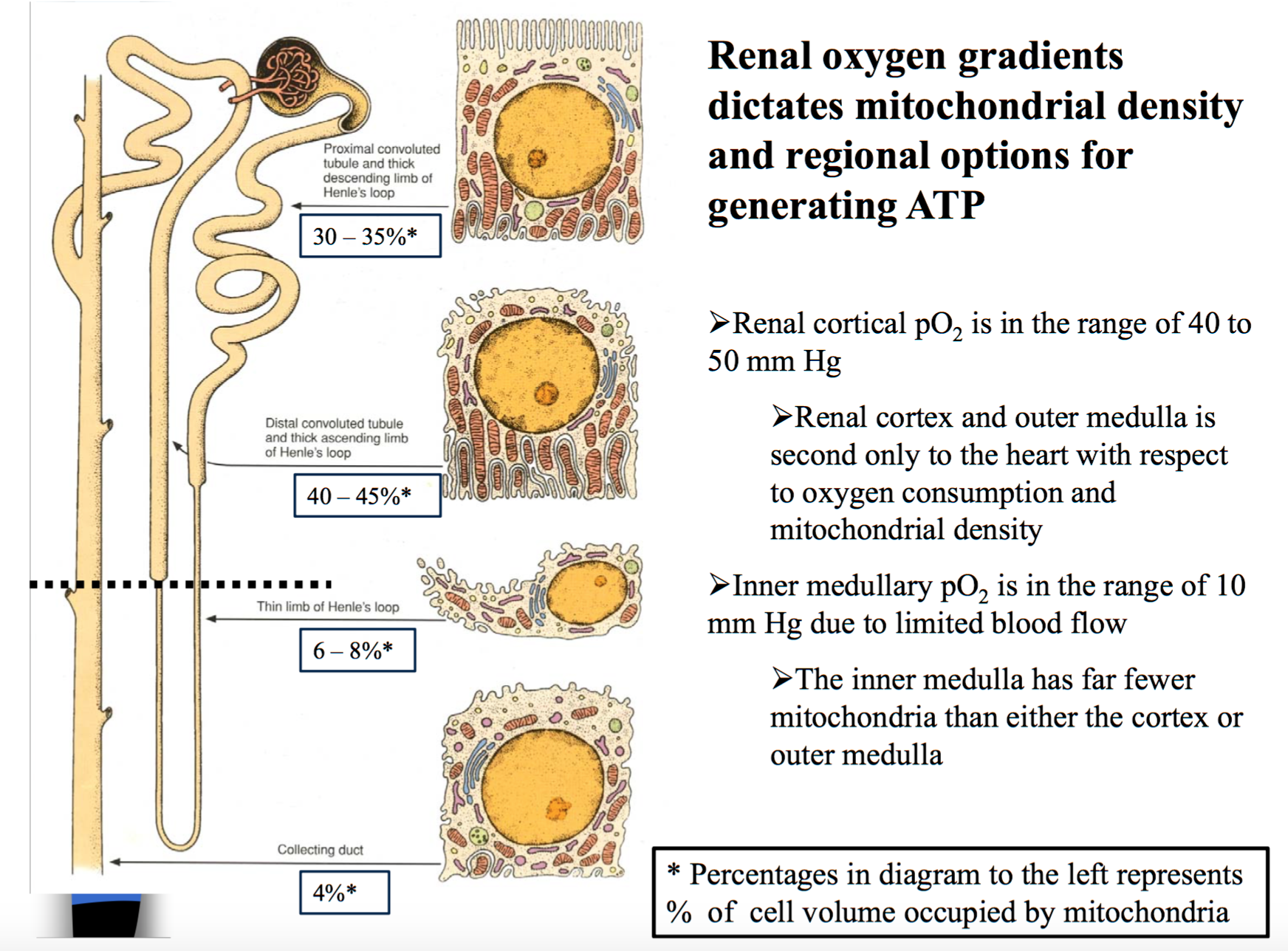
Kidney local pO 2
Kidney Biochemistry

Cubilin and Megalin binding properties
.
.

The megalin- and cubilin-mediated uptake of three vitamin carrier protein complexes: vitamin D binding protein (DBP)-vitamin D3, transcobalamin (TC)-vitamin B12, and retinol binding protein (RBP)-retinol in renal proximal tubule. Following receptor-mediated endocytosis via apical coated pits, the complexes accumulate in lysosomes for degradation of the proteins, while the receptors recycle to the apical plasma membrane via dense apical tubules. As illustrated here and detailed in the text, megalin mediates the uptake of cubilin and its ligands. Whether the two receptors are constitutively associated in the plasma membrane and remain associated during recycling in dense apical tubules is not known. Whereas TC and RBP apparently bind exclusively to megalin, DBP binds with similar affinity to both megalin and cubilin. The intracellular processing of the vitamins may include modifications such as hydroxylation of 25(OH)D3 to 1,25-(OH)2D3, and metabolism of B12. The mechanisms for the cellular release of the vitamins remain to be clarified.
The tandem endocytic receptors megalin and cubilin are important proteins in renal pathology, 2002