
Theanine, also gamma-glutamylethylamide or 5-N-ethyl-glutamine, is an amino acid and a glutamic acid analog commonly found in tea (infusions of Camellia sinensis), primarily in green tea, and also in the basidiomycete mushroom Boletus badius and in guayusa. More specifically, this compound is called L-theanine, being the L- amino acid In 1950, the tea laboratory of Kyoto successfully separated theanine from gyokuro leaf.
Theanine is an analog to glutamine and glutamate. It is absorbed in the intestinal brush-border membrane in the small intestine by a Na(+)-dependent cotransporter. Once absorbed, free L-theanine in the bloodstream can cross the blood–brain barrier .
L-Theanine can improve mood, reduce stress and help focus and particularly when working with caffeine. Moreover, individuals taking Theanine also showed improved alpha wave activity, the activity present when you are alert but not stressed and for most people the most desirable awake state. Theanine has been found to increase dopamine in humans.The effects of L-theanine parallel the role of GABA neurotransmission, regulating a delicate interplay between excitation and inhibition. These inhibitory signals are essential for the regulation of mood, memory, attention and relaxation in our cognitive framework.
A single cup of tea is estimated to contain about 20 mg of L-theanine, whereas effective dosage for most studies is 200 mg.
There is a large base of clinical trials done by the Japanese to indicate that Theanine is not only effective but also safe. Japan approved Theanine as a universally safe supplement as early as 1964 and permitted unrestricted amounts in all foods except those for infants.
It is sold in the US as a dietary supplement, and is classified by the FDA as a generally recognized as safe (GRAS) ingredient.
Effects on the brain
Able to cross the blood–brain barrier, theanine has psychoactive properties: reduce mental and physical stress, improve cognition and boost mood in a synergistic manner with caffeine.
Mechanism of action and Neuroprotective benefits:
The underlying mechanism of L-theanine is to increase inhibitory neurotransmitter levels as well as act directly to block overproduction of excitatory neurotransmitters.
L-theanine is a glutamic acid analog, a compound chemical similar to the neurotransmitter glutamate. Excessive glutamate can be neurotoxic and induce cell death, contributing to the cognitive declines in dementia and stroke patients. L-theanine’s neuroprotective roles are two-fold. First, the chemical resemblance of L-theanine to glutamate permits competitive binding to post-synaptic receptors, inhibiting binding of glutamate. Secondly, L-theanine binds to the glutamate transporter to prevent reuptake and decrease available glutamate. Theanine also acted on glutamine (Gln) transporter strongly and inhibited the incorporation of extracellular Gln into neurons, which in turn suppressed the conversion of Gln to glutamate by glutaminase This process mediates the neuroprotective function of L-theanine in stressed cells.
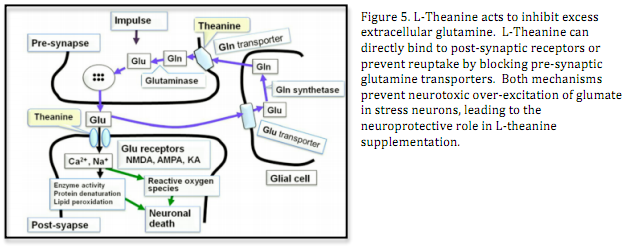
L-Theanine primary effect seems to increase the overall level of the brain inhibitory transmitter GABA. It also increases brain dopamine levels and has a low affinity for AMPA, kainate and NMDA receptors.
Oral intake of L-Theanine could cause anti-stress effects via the inhibition of cortical neuron excitation.
Neuroprotective effects of theanine and its preventive effects on cognitive dysfunction.
L-Theanine reduces psychological and physiological stress responses
Wikipedia
L-theanine and alpha-band oscillatory brain activity:
Alpha-band oscillations (8-14 Hz) indicate a relaxed, but attentive state. Using EEGs, researchers examined differences in alpha-band activity during a demanding attention task where individuals were given either 250 mg L-theanine or a placebo. A robust increase in attention related alpha-band signal was recorded in those administered L-theanine. Furthermore, topographic analysis showed increased activity localized to right hemispheric posterior parietal cortex. These findings support a strong psychoactive effect of L-theanine, specifically on visual attention.
L-Theanine promotes Alpha wave generation in the brain, an awake, alert and relaxed physical and mental condition is achieved which demonstrates Theanine’s effectiveness in stress management.
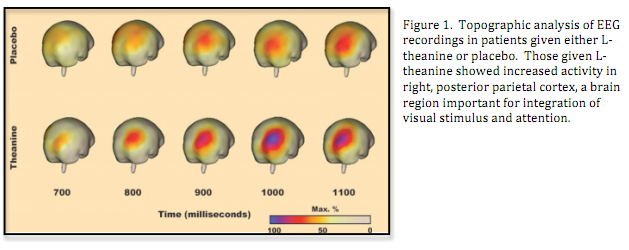
The effects of L-theanine on alpha-band oscillatory brain activity during a visuo-spatial attention task.
L-theanine, a natural constituent in tea, and its effect on mental state
L-theanine and caffeine:
Current research shows that combination of L-theanine and caffeine produces a synergistic effect and mediates cognitive benefits. A study of healthy adults given either L-theanine (100mg), L-theanine(100 mg) + caffeine(50 mg), or placebo, reported that only the L-theanine combination produces significant results in response time and correct answer frequency during a memory and attention-switching task. These results replicate previous evidence which suggests that L-theanine and caffeine in combination are beneficial for improving performance on cognitively demanding tasks.
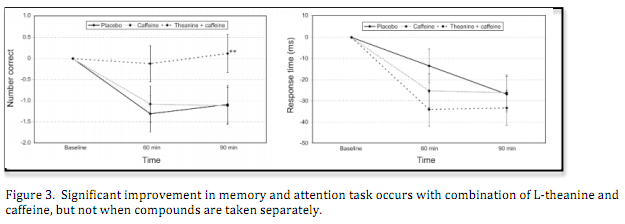
The combined effects of L-theanine and caffeine on cognitive performance and mood.
L-theanine increases the inhibitory neurotransmitter, glycine:
Glycine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter with analogous properties to GABA. An L-theanine supplement can directly elevate glycine concentration in the brain. Furthermore glycine promotes the release of dopamine within the striatum, a part of the telencephalon receiving input from the cortex to modulate behavior. L-theanine’s mood regulating properties and balance of neurotransmission are hypothesized to directly result from elevated glycine.
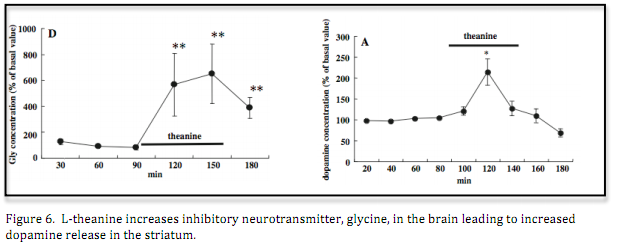
Theanine, gamma-glutamylethylamide, a unique amino acid in tea leaves, modulates neurotransmitter concentrations in the brain striatum interstitium in conscious rats.
Immune system effects
Human gammadeltaT lymphocytes are a subset of T cells and are a first line of defense against microbes and tumors. These gammadeltaT cells can be primed by certain short-chain alkylamines. These primed gammadeltaT cells have an enhanced capacity to proliferate and to secrete cytokines upon ex vivo exposure to a wide variety of microbes and tumor cells. The largest dietary source of alkylamines is L-theanine, an amino acid unique to tea beverages that is catabolized to ethylamine. Supplementation of subjects with capsules containing L-theanine and catechins has recently been shown to decrease the incidence of cold and flu symptoms, while enhancing gammadeltaT cell function. A study, published in 2003, included a four-week trial with 11 coffee drinkers and 10 tea drinkers, who consumed 600 milliliters of coffee or black tea daily. Blood sample analysis found the production of antibacterial proteins was up to five times higher in the tea drinkers, an indicator of a stronger immune response.
L-theanine intervention enhances human gammadeltaT lymphocyte function.
Circulatory system effects
Consumption of tea (Camellia sinensis) improves vascular function and is linked to lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease. Endothelial nitric oxide is the key regulator of vascular functions in endothelium.A study demonstrates that l-theanine, a non-protein amino-acid found in tea, promotes nitric oxide (NO) production in endothelial cells. These results demonstrated that l-theanine administration in vitro activated ERK/eNOS resulting in enhanced NO production and thereby vasodilation in the artery. The results of our experiments are suggestive of l-theanine mediated vascular health benefits of tea.
L-Theanine promotes nitric oxide production in endothelial cells through eNOS phosphorylation.
Therapeutic uses and chemotherapy
There have not been any side effects reported from taking L-theanine. However, drinking large amounts of green tea in general may cause upset stomach, irritability, and nausea due to the tea’s caffeine content. Also, do not take L-theanine if undergoing chemotherapy or are taking lipid-lowering medicines or sedatives, since L-theanine may alter the effects of these drugs. L-theanine has been shown to increase the anti-tumor activity of two cancer-fighting drugs, doxorubicin and idarubicin:it improve the efficacy of cancer treatments by decreasing the amount of cancer drug in healthy cells while focusing the drug on cancerous cells. Therefore theanine selectively moderates the chemotherapeutic agent induced toxicities.
Theanine is known to reduce blood pressure and if taking theanine supplements with blood pressure medication the potential exists to reduce blood pressure too far.
Many studies had individuals consuming as much as 200 mg of L-Theanine a day although some limited the amounts to 50 – 100 mg per day. It is wisest to follow label directions and consult with a physician if unsure of the appropriate dosage for a specific individual. L-Theanine supplement can be obtained in capsule or tablet form.

Effects of theanine on alcohol metabolism and hepatic toxicity.
Combination of theanine with doxorubicin inhibits hepatic metastasis of M5076 ovarian sarcoma..
Improvement of idarubicin induced antitumor activity and bone marrow suppression by theanine, a component of tea..
Main characteristics of theanine :
- Promoting relaxation without causing drowsiness
- Improving learning and concentration
- Heightening mental acuity
- Supporting the Immune System
- Reducing stress and anxiety
- Reducing cardiovascular risks
- Long-term neuroprotection
Conclusion:
The health benefits and effects of L-theanine are well studied and include relaxation, alertness, memory improvements, increased attention, increased immunity, and long-term neuroprotection. L-Theanine can cross the blood-brain barrier and mediate inhibitory neurotransmission. This inhibition produces profound cognitive effects by moderating glutamate excitation, increasing glycine levels, and elevating dopamine release. Ultimately L-theanine promotes a balancing of excitation in important brain regions.