DEFINITION
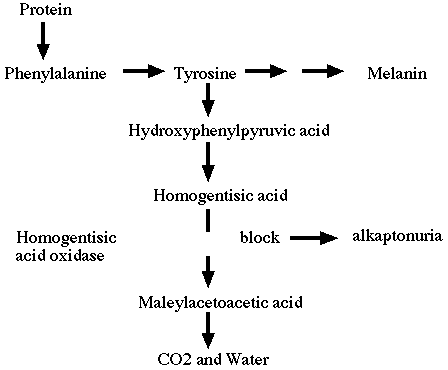
Alkaptonuria (black urine disease or alcaptonuria) is a rare inherited genetic disorder of phenylalanine and tyrosine metabolism . This is an autosomal recessive condition that is due to a defect in the enzyme homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase , which participates in the degradation of tyrosine. As a result, homogentisic acid and its oxide , called alkapton, accumulate in the blood and are excreted in urine in large amounts (hence -uria) and deposits in connective tissues causing a debilitating arthritis.
(The molecular basis of alkaptonuria,1996)
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Clinical manifestation, blue-black pigmentation of connective tissues, usually appears after age 30 while the development of arthritis, particularly in the spine and large joints, beginning in early adulthood.
(Alkaptonuria,2013)
Alkaptonuria is found relatively frequently in Slovakia, Eastern Czechoslovakia (1 in 25,000 inhabitants) cause of the genetic isolation in the past.The normal prevalence is between 1:100,000 and 1:250,000 people worldwide.It is reported frequently in the Dominican Republic, but exact prevalence there is not known.
(Alkaptonuria,1979)
(Alkaptonuria in Slovakia: thirty-two years of research on phenotype and genotype,2002)
(Alkaptonuria,2003)
SYMPTOMS

The main symptoms of alkaptonuria are due to the accumulation in tissues of homogentisic acid and its oxidized derivatives in polymerized form.
Alkaptonuria is often asymptomatic, but the sclera of the eyes may be pigmented. The skin may be darkened in ear, sun-exposed areas and around sweat glands; sweat may be coloured brown. Urine and ear wax may turn brown or even inky black if collected and left exposed to open air.
(Alkaptonuria,2011)
In the joints, the accumulation of homogentisic acid leads to cartilage damage (degenerative peripheral ochronosis) specifically in the spine, leading to low back pain at a young age in most cases.
(Alkaptonuria,2013)
(Alkaptonuria, ochronosis, and ochronotic arthropathy,2004)
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis of alkaptonuria needs to be suspected before diagnostic testing can be performed using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. Both blood plasma and urine (urinalysis) can be used for diagnosis. In healthy subjects, homogentisic acid is absent in both blood plasma and urine. In alkaptonuria, plasma levels are 6.6 micrograms/ml on average, urine levels are on average 3.12 mmol/mmol of creatinine and if ferric chloride is added to the urine, it will turn the urine a black color in patients with this condition. Darkening of urine is the only sign of the disorder in the pediatric age group, and it occurs at very early stage.
(Alkaptonuria,2011)
(From darkening urine to early diagnosis of alkaptonuria,2008)
(Alkaptonuria,2013)
In individuals older than age 40 years, other helpful tests can be echocardiography to detect aortic dilation, aortic or mitral valve calcification and stenosis; CT to detect coronary artery calcification.
(Alkaptonuria,2013)
PATHOGENESIS

Homogentisic acid is a natural intermediary of the metabolism of tyrosine. Hepatic homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase (coded by the HGD gene) metabolises homogentisic acid into 4-maleylacetoacetate. Alkaptonuria arises in people who have inherited, in an autosomal recessive manner, two abnormal HGD genes: one from each parent. Numerous different HGD mutations have been identified.
(Alkaptonuria,2011)
(The molecular basis of alkaptonuria,1996)
(Alkaptonuria,2013)
(Mutation spectrum of homogentisic acid oxidase (HGD) in alkaptonuria,2009)
(Molecular defects in alkaptonuria,1997)
Coinheritance of either neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism or sucrase-isomaltase deficiency and alkaptonuria provided a candidate location for the mutated genes on chromosome 3. Homozygosity mapping with polymorphic loci identified a 16 centiMorgan region on chromosome 3q that contains the alkaptonuria gene.
(Homozygosity mapping of the gene for alkaptonuria to chromosome 3q2,1993)
(Alkaptonuria,2003)

In a patient who underwent a liver transplant for an unrelated problem, alkaptonuria resolved and joint disease stabilised after the transplant, confirming that the liver is the main site of homogentisic acid production in alkaptonuria.
(Ochronotic arthropathy: disappearance of alkaptonuria after liver transplantation for hepatitis B-related cirrhosis,2005)
PATIENT RISK FACTORS
Genetic
Alkaptonuria is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means it is passed down from parents to their children. It was the first disease to be interpreted as a mendelian recessive trait by Garrod in 1902. If both parents carry one copy of the defective gene related to this condition, they typically do not show signs and symptoms but each of their children has a 25% chance of developing the disease.
(Alkaptonuria,2013)
(The molecular basis of alkaptonuria,1996)
COMPLICATIONS

(Alkaptonuric Ochronosis with Aortic Valve and Joint Replacements and Femoral Fracture A Case Report and Literature Review,2004)
The build-up of homogentisic acid in the cartilage causes arthritis in about 50% of older adults with alkaptonuria, involving, over the spine, the large peripheral joints (hip and shoulder).
Kidney stones and stone formation in the prostate (in men) are common as valvular heart disease and coronary artery disease like pigment deposition, aortic or mitral valve calcification or regurgitation and occasionally aortic dilatation.
Testing for the presence of elevated urinary HGA in sibs of affected individuals allows early diagnosis and intervention to prevent secondary complications.
(Alkaptonuria,2013)
(Alkaptonuria,2013)
THERAPY
Commonly recommended treatments include large doses of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) that decrease the build-up of brown pigment in the cartilage and may slow the development of arthritis.
(Alkaptonuria,2013)
(From darkening urine to early diagnosis of alkaptonuria,2008)
Dietary restriction of phenylalanine and tyrosine intake may be effective in children, but benefits in adults have not been demonstrated.
(From darkening urine to early diagnosis of alkaptonuria,2008)
(The success of dietary protein restriction in alkaptonuria patients is age-dependent,1998)
The herbicide nitisinone inhibits 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase, the enzyme that generates homogentisic acid from 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid. This reduces homogentisic acid. The main side-effect is irritation of the cornea, and there is a concern that it will cause the symptoms of hereditary tyrosinaemia type III because of the possible accumulation of tyrosine or other intermediaries.
(Use of nitisinone in patients with alkaptonuria,2005)
(Natural history of alkaptonuria,2002)
In case of complications, physical and occupational therapy to help maintain muscle strength and flexibility, knee, hip, and shoulder replacements, surgical intervention for prostate stones and renal stones and valve replacement were needed.
Patients had to avoid: physical stress to the spine and large joints, including heavy manual labor or high-impact sports, to try to reduce progression of severe arthritis.
(Alkaptonuria,2013)

A pre-clinical study of potential antioxidative therapies for alkaptonuria is proposed. This study is based on using the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) administered in combinations with ascorbic acid (ASC). In these way, it has been proven that NAC counteracts the side-effects of ASC in vitro cell model, using human articular primary chondrocytes challenged with an excess of HGA (0.33 mM). A significantly improvement in efficacy was found especially for the treatment of ochronotic arthropathy.
(Evaluation of antioxidant drugs for the treatment of ochronotic alkaptonuria in an in vitro human cell model,2010)