SARS-CoV-2: Olfaction, Brain Infection, and the Urgent Need for Clinical Samples Allowing Earlier Virus Detection. 2020
Multiple non-neuronal cell types present in the olfactory epithelium express two host receptors, ACE2 and TMPRSS2 proteases, that facilitate SARS-CoV-2 binding, replication, and accumulation.
Olfactory neuron as a sensor of viral attack. Anosmia = mild disease
Intriguingly, older patients who are known to be much more sensitive to SARS-CoV-2 infection are also those who have their sense of smell compromised simply because of their age. Reduced numbers of ORNs in older people can potentially slow down their early immune response and, consequently, lead to more severe COVID-19 symptoms.
progesterone+and+olfactory
progestin receptors in olfactory organs and sperm motility

Olfactory G proteins: Simple and complex signal transduction, 1998
Olfactory, Taste, and Photo Sensory Receptors in Non-sensory Organs: It Just Makes Sense, 2018
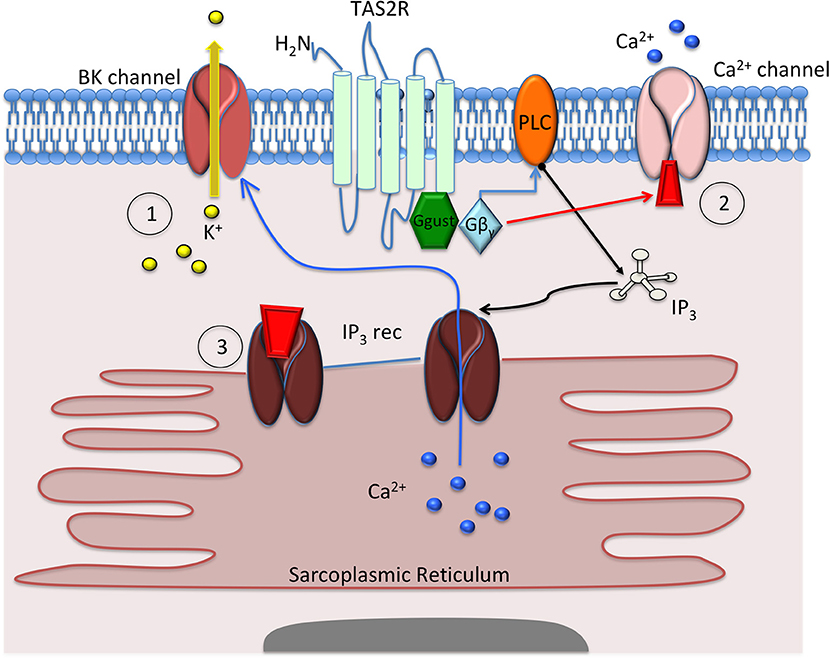
Mechanisms proposed to explain how bitter taste receptor (TAS2R) agonists cause airway smooth muscle (ASM) cell relaxation. Deshpande et al. (1) proposed that activation of the TAS2R caused activation of gusticin, followed by Gβγ and phospholipase C (PLC) subunits, to activate inositol triphosphate (IP3), which in turn activates the IP3 receptor to release calcium (Ca2+) from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This release of calcium causes opening of the BKCa-channel and efflux of potassium (K+) that hyperpolarizes and relaxes the ASM cell. Zhang et al. (2) proposed that TAS2R activation leads to small, incremental increases in Ca2+, which causes closure of membrane Ca2+ channels. This closure inhibits Ca2+ influx, cell depolarization, and cell contraction, leading to cellular relaxation. Tan et al. (3) proposed that TAS2R activation causes a change in Ca2+ sensitivity and/or changes to Ca2+ oscillation that inhibit Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, thereby inhibiting cellular contraction.

Figure 5-17. Olfactory signal processing. (a) Detail of the olfactory epithelium, a mixture of olfactory sensory and supporting cells. Cilia of the sensory neurons, exposed to the mucus layer, carry the olfactory receptors (each neuron one type of receptor). (b) The signaling cascade in an olfactory sensory neuron cilium starts with the activation of the olfactory G-protein. The Gαolf (GNAL) bound to GTP attaches to and activates adenylyl cyclase-3, resulting in the production of cAMP. This causes an increase in conductivity of the cyclic nucleotide-sensitive cation channel (a heterotetramer composed of CNGA2, A4, and B1b) leading to entry of Na+ and Ca2+. The increased cytosolic Ca2+ opens the ANO3 chloride channel and this causes the membrane depolarization that leads to the release of histamine at the synaptic terminal. © These two dose–response curves illustrate nicely the cascades of signal amplification. Raising the cAMP brings about the opening of the CNG channel and the ensuing rise in Ca2+ opens the Cl− channels, which are so abundantly expressed that they bring about a strong membrane depolarization.
Odorant receptor and sperm
OR51E2
Olfactory receptor (PubMed:29249973, PubMed:27226631). Activated by the odorant, beta-ionone, a synthetic terpenoid (PubMed:29249973, PubMed:27226631, PubMed:19389702). The activity of this receptor is propably mediated by G-proteins leading to the elevation of intracellular Ca2+, cAMP and activation of the protein kinases PKA and MAPK3/MAPK1 (PubMed:27226631, PubMed:29249973). Stimulation of OR51E2 by beta-ionone affects melanocyte proliferation, differentiation, and melanogenesis (PubMed:27226631). Activation of OR51E2 by beta-ionone increases proliferation and migration of primary retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells (PubMed:29249973). Activated also by the short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) acetate and propionate. In response to SCFA, may positively regulate renin secretion and increase blood pressure (PubMed:23401498). May also be activated by steroid hormones and regulate cell proliferation (PubMed:19389702). Activated by L-lactate in glomus cells (By similarity)
OR7d4
Odorant receptor. Selectively activated by androstenone and the related odorous steroid androstadienone.
Odorant receptor which may be involved in sperm chemotaxis. Bourgeonal is a strong chemoattractant for sperm in vitro and is shown to be a strong agonist for OR1D2 in vitro. May also function in olfactory reception
ACE2, angiotensin-(1–7), and Mas: the other side of the coin. 2013
The renin–angiotensin system (RAS) has recently been extended by the addition of a novel axis consisting of the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the heptapeptide angiotensin (1–7) (Ang-(1–7)), and the G protein-coupled receptor Mas.