Regulatory T cells, sometimes known as suppressor T cells, are a specialized subpopulation of T cells which suppresses activation of the immune system and thereby maintains tolerance to self-antigens.
Induction
Factors that have been described to be important for Treg induction within the tumor include TGF-b, IL-10, H-Ferritin (Gray CP, Arosio P, Hersey P. Heavy chain ferritin activates regulatory T cells by induction of changes in dendritic cells. Blood 2002;99:3326–34), IDO and Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2).9,20–22 These findings highlight the importance of
understanding the mechanisms of immune-escape in the tumor microenvironment.
Follicular lymphoma B cells induce the conversion of conventional CD41 T cells to T-regulatory cells
Treg cells glucocorticoids

Tregs cAMP PTH
Regulatory T-Cell-Mediated Suppression of Conventional T-Cells and Dendritic Cells by Different cAMP Intracellular Pathways.
Cell junction and cycle AMP: III. Promotion of junctional membrane permeability and junctional membrane particles in a junction-deficient cell type.
caffeine and serum cAMP
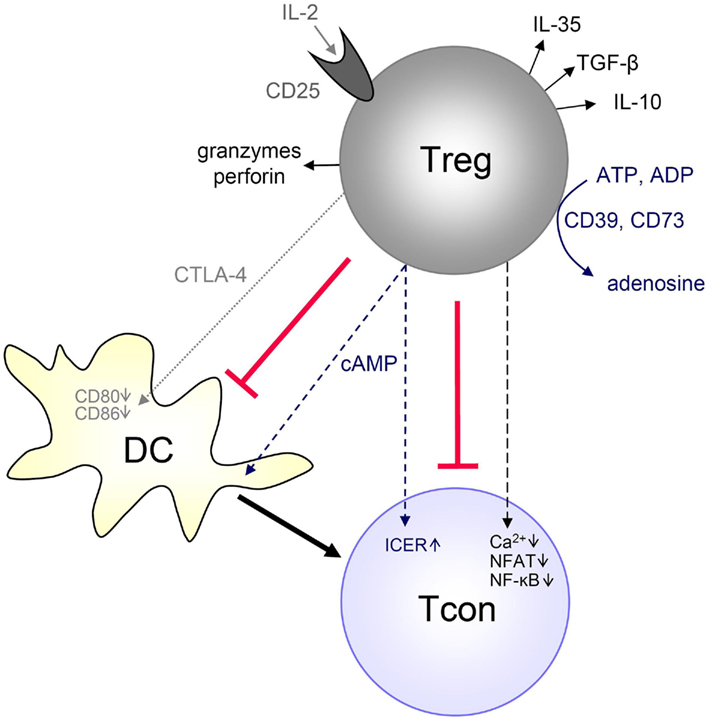
Molecular mechanisms of Treg-mediated T cell suppression 2012
CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) can suppress other immune cells and, thus, are critical mediators of peripheral self-tolerance. On the one hand, Tregs avert autoimmune disease and allergies. On the other hand, Tregs can prevent immune reactions against tumors and pathogens. Despite the importance of Tregs, the molecular mechanisms of suppression remain incompletely understood and controversial.

