The lymphatic system consists of lymphatic organs, a conducting network of lymphatic vessels, and the circulating lymph.
The lymphatic system at Course Hero


Lymphatic vessels are thin-walled, valved structures that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscles, and adventitia that bind the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues.
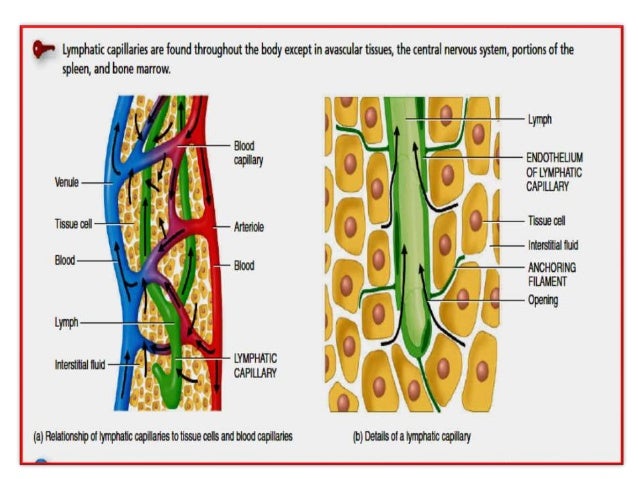

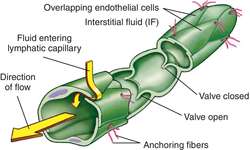
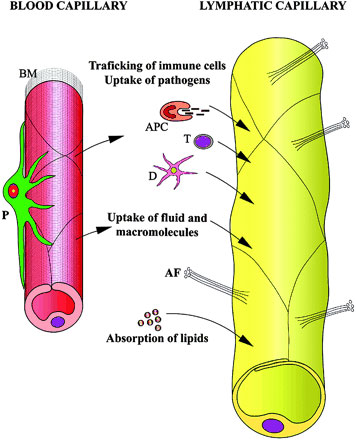
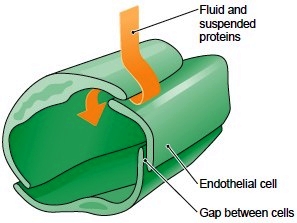
Fluid and proteins can enter the capillary with ease through gaps between the endothelial cells. Overlapping cells act as valves to prevent the material from leaving.
Movement of Lymph
The segments of lymphatic vessels located between the valves contract rhythmically, propelling the lymph along. The contraction rate is related to the volume of fluid in the vessel. As skeletal muscles contract during movement, they compress the lymphatic vessels and drive lymph forward. Changes in pressures within the abdominal and thoracic cavities caused by breathing aid the movement of lymph during passage through these body cavities.

Lymphatic Vessels, Inflammation, and Immunity in Skin Cancer, 2016
permeability/Permeation
Increased expression and activation of gelatinolytic matrix metalloproteinases is associated with the progression and recurrence of human cervical cancer. 2003
Lymph
The mesenteric lymph duct cannulated rat model: application to the assessment of intestinal lymphatic drug transport., 2015
Macrophages are important mediators of either tumor- or inflammation-induced lymphangiogenesis. 2011
Fluid exchange across endothelium. 1997
Protein expression profiles of human lymph and plasma mapped by 2D-DIGE and 1D SDS-PAGE coupled with nanoLC-ESI-MS/MS bottom-up proteomics. 2013
- The 1DEF coupled with nanoLC-MS-MS revealed that the common proteome between the two biological fluids (144 out of 253 proteins) was dominated by complement activation and blood coagulation components, transporters and protease inhibitors. The enriched proteome of human lymph (72 proteins) consisted of products derived from the extracellular matrix, apoptosis and cellular catabolism. In contrast, the enriched proteome of human plasma (37 proteins) consisted of soluble molecules of the coagulation system and cell-cell signaling factors.
Figure
The primary or central lymphoid organs generate lymphocytes from immature progenitor cells.
The thymus and the bone marrow constitute the primary lymphoid organs involved in the production and early clonal selection of lymphocyte tissues. Bone marrow is responsible for both the creation of T cells and the production and maturation of B cells. From the bone marrow, B cells immediately join the circulatory system and travel to secondary lymphoid organs in search of pathogens. T cells, on the other hand, travel from the bone marrow to the thymus, where they develop further. Mature T cells join B cells in search of pathogens. The other 95% of T cells begin a process of apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death.