Thyroid hormones are sintethyzed from tyrosil residues of thyroglobin. Another important passage is their iodinization. Then thyroid hormones are released in blood stream and only in peripheral tissues they are transformed and activated.
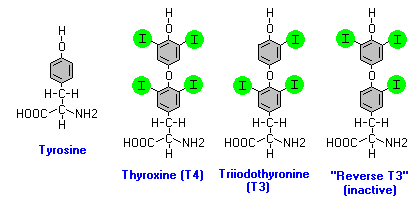
Among the thyroid hormones the most active is thyronine (T3), whereas thyroxine (T4) is the store that circulates in blood linked to TBG, TTR, albumin. Instead of rT3, an isomer of thriiodothyronine(T3), is the inactivated from obtained by the deiodase III activity which tranforms 40% of T4 to rT3. But in any situation when body needs to conserve energy and focus on something else, it will change the above percentages, changing the conversion of rT3 to 50% or more. Examples are emotional, physical, or biological stress. If rT3 levels increase in the organism, it's a problem as rT3 binds T3 receptor sites, blocking the good effects and making the patient hypo. Increase T4 and rT3 levels and diminished T3 ones correlates with decreased physical functioning and a catabolic state, with a bigger risk to develope obesity.
Studies demostrate tath patients with low T3 syndrome (with high rT3) have the lowest PPS( scoring system that takes into account normally activity of daily living and is a mesure of physical and mental activity.
Thyroid Hormone Concentrations, Disease, Physical Function, and Mortality in Elderly Men, 2005
Moreover rT3 blocks T4 to T3 conversion
A Study of Extrathyroidal Conversion of Thyroxine (T4) to 3,3',5-Triiodothyronine (T3) in Vitro, 1977

Some studies evidence different availability of them during particular states of the organism as acidosis. Children in acidotic state have been compared to healthy one with the result of the same TSH, lower T4 and T3 and higher rT3 serum levels.
Thyroid hormones changes in infants and children with metabolic acidosis, 1991
Equally it happens in ketoacidosis.
A low T3 syndrome in diabetic ketoacidosis, 1978
Infants could show ketosis after fever. And fever intensifies lipid peroxidation processes leading to a decrease in 5'-monodeiodinase activity.
Fever induced oxidative stress: the effect on thyroid status and the 5'-monodeiodinase activity, protective role of selenium and vitamin E, 2001
The Nuclear Receptor Constitutively Active/ Androstane Receptor Regulates Type ! Deyodinaseand Thyroid Hormone Activity in the Regenerating Mouse Liver, 2006
When the patient has a diminished affinity of hemoglobin to oxigen, due to acidosis, thyroid hormones decrease. Just when there is more requirement. Infact physiologically as the thyroid is vascolarized a lot, it's a sort of oxigen detector of the organism. However ketosis opposites to the needs of an increasing secretion of T4 and T3 and the activity of deiodinase.
The consequences are similar to ipothyroidism which is releated to a lower synthesis of cytochrome C. The organism obtains a part of the cytocrome from cholesterol, whom metabolism is inducced by T3. And their function is of fundamental importance in tissues respiration and production of energy.
Requirement for thyroid hormone receptor beta in T3 regulation of cholesterol metabolism in mice, 2002