Phosphorus is an essential mineral that is required by every cell in the body for normal function
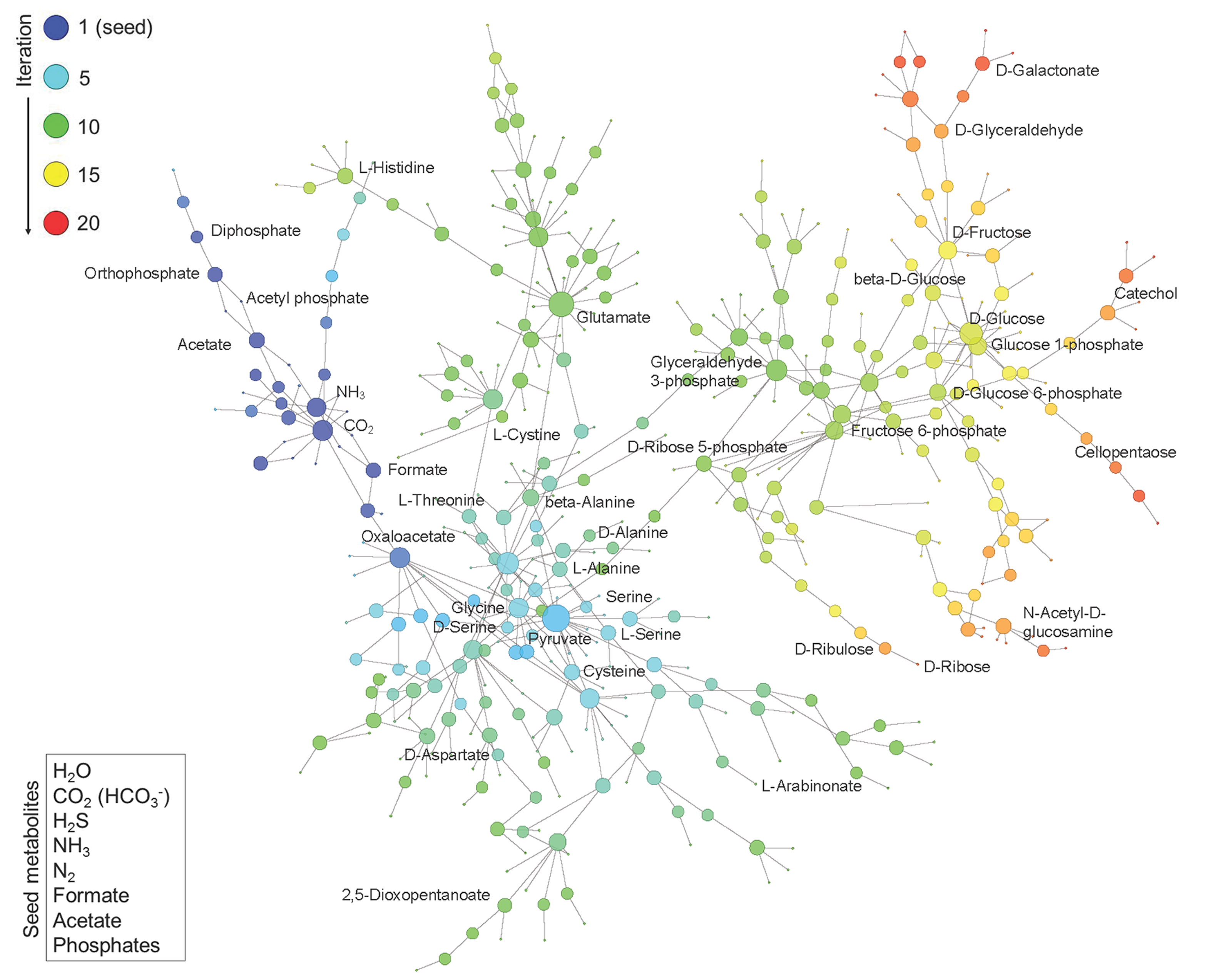
Construction of Phosphorus-Dependent Metabolic Network. Network expansion simulation was executed using a set of defined seed compounds (bottom left box) and all balanced reactions in the background metabolism pool derived from the updated KEGG reactions. The figure displays the obtained phosphorus-dependent network in which metabolites are linked if they have a reactant-product relationship during the expansion. The metabolites generated at different iteration steps during the network expansion process are represented by nodes in different colors. The size of the node represents the degree of the node, i.e., the number of reactions added in the subsequent iteration
Phosphates as Energy Sources to Expand Metabolic Networks, 2019
Avian multiple inositol polyphosphate phosphatase is an active phytase that can be engineered to help ameliorate the planet’s “phosphate crisis”

Effect of dietary phosphate

Factors affecting intestinal absorption
Factors affecting renal handling
Phosphatonins
Biological effects of FGF-23 and sFRP-4 on Na+-dependent Pi transport in Kidney cells (Role of PIPR sequence: arginine (I) is a Pin sensor?)

ref 2008
FGF-23 causes a redistribution and internalization of Na+-Pi IIa cotransporters on the surface of renal epithelial cells
Regulation of Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 Signaling by Klotho 2006

Ca P Klotho 2008
Mutations of the FGF23 gene found in patients with ADHR occur either in arginine176 or arginine179 just before the processing site of FGF23. Because these arginine residues are part of the arginine-X-X-arginine sequence recognized by furin-family endopeptidase, it was
anticipated that these mutations affect proteolytic processing of FGF23. Actually, when mutant FGF23 proteins found in patients with ADHR were expressed in vitro and analyzed by Western blotting, these proteins were shown to be resistant to the processing (REF 2005).
FGF-23(R176Q) suppressed 1alpha-hydroxylase mRNA and activated the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. The MAPK inhibitor PD98059 effectively abolished FGF-23-induced suppression of 1alpha-hydroxylase mRNA by blocking signal transduction via ERK1/2. REF 2007



Mechanism of action of sFRP-4. The secreted frizzled related proteins function as antagonists of the Wnt proteins. We demonstrated that the infusion of sFRP-4 into rats was associated with phosphaturia, a concomitant increase in the amount of phospho-β-catenin, and a decrease in the amount of nonphosphorylated β-catenin. Thus, sFRP-4 antagonizes Wnt signaling in the kidney. Infusion of sFRP-4 decreases Na+-Pi cotransporter abundance in the brush border membrane of the proximal tubule and reduced surface expression of the Na+-Pi IIa cotransporter in the proximal tubules
SFRP-4 abrogates Wnt-3a-induced beta-catenin and Akt/PKB signalling and reverses a Wnt-3a-imposed inhibition of in vitro mammary differentiation 2008
 Papers FGF23 and VDR
Papers FGF23 and VDR
Proteomic analysis of alterations in the secretome of Arabidopsis thaliana suspension cells subjected to nutritional phosphate deficiency 2008
Biochemistry. 2009 Aug 4;48(30):7140-9.
Succinyl-CoA synthetase is a phosphate target for the activation of mitochondrial metabolism. 2009
Phillips D, Aponte AM, French SA, Chess DJ, Balaban RS.
Succinyl-CoA synthetase (SCS) is the only mitochondrial enzyme capable of ATP production via substrate level phosphorylation in the absence of oxygen, but it also plays a key role in the citric acid cycle, ketone metabolism, and heme synthesis. Inorganic phosphate (P(i)) is a signaling molecule capable of activating oxidative phosphorylation at several sites, including NADH generation and as a substrate for ATP formation. In this study, it was shown that P(i) binds the porcine heart SCS alpha-subunit (SCSalpha) in a noncovalent manner and enhances its enzymatic activity, thereby providing a new target for P(i) activation in mitochondria. Coupling 32P labeling of intact mitochondria with SDS gel electrophoresis revealed that 32P labeling of SCSalpha was enhanced in substrate-depleted mitochondria. Using mitochondrial extracts and purified bacterial SCS (BSCS), we showed that this enhanced 32P labeling resulted from a simple binding of 32P, not covalent protein phosphorylation. The ability of SCSalpha to retain its 32P throughout the SDS denaturing gel process was unique over the entire mitochondrial proteome. In vitro studies also revealed a P(i)-induced activation of SCS activity by more than 2-fold when mitochondrial extracts and purified BSCS were incubated with millimolar concentrations of P(i). Since the level of 32P binding to SCSalpha was increased in substrate-depleted mitochondria, where the matrix P(i) concentration is increased, we conclude that SCS activation by P(i) binding represents another mitochondrial target for the P(i)-induced activation of oxidative phosphorylation and anaerobic ATP production in energy-limited mitochondria.
XPo proteins in Drosophila

A phosphate-sensing organelle regulates phosphate and tissue homeostasis, 2023