Coenzyme A is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle.
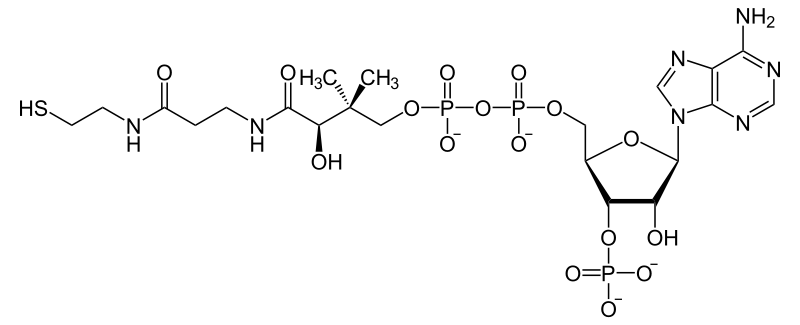
All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester, such as acetyl-CoA) as a substrate.
SYNTHESIS AND TURNOVER
In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires:
- cysteamine
- pantothenate
- adenosine triphosphate.

Protein Aminoacids Percentage (Width 700 px)


Apparently from the evolutionary point of view the sequence is from the last to the first


CELLULAR FUNCTIONS
cellular localization,
biological function
REGULATION
In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires:
- cysteamine
- pantothenate
- adenosine triphosphate.
Coenzyme+A+and+AMPK
- Activation of AMP kinase and inhibition of Rho kinase induce the mineralization of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells through endothelial NOS and BMP-2 expression. 2008
- Activation of AMPK suppresses 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl (HMG)-coenzyme A (CoA) reductase.
- Pharmacological stimulation of NADH oxidation ameliorates obesity and related phenotypes in mice. 2009
- OBJECTIVE: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotides (NAD+ and NADH) play a crucial role in cellular energy metabolism, and a dysregulated NAD+-to-NADH ratio is implicated in metabolic syndrome. However, it is still unknown whether a modulating intracellular NAD+-to-NADH ratio is beneficial in treating metabolic syndrome. We tried to determine whether pharmacological stimulation of NADH oxidation provides therapeutic effects in rodent models of metabolic syndrome.
RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS: We used β-lapachone (βL), a natural substrate of NADH:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), to stimulate NADH oxidation. The βL-induced pharmacological effect on cellular energy metabolism was evaluated in cells derived from NQO1-deficient mice. In vivo therapeutic effects of βL on metabolic syndrome were examined in diet-induced obesity (DIO) and ob/ob mice.
RESULTS: NQO1-dependent NADH oxidation by βL strongly provoked mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation in vitro and in vivo. These effects were accompanied by activation of AMP-activated protein kinase and carnitine palmitoyltransferase and suppression of acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylase activity. Consistently, systemic βL administration in rodent models of metabolic syndrome dramatically ameliorated their key symptoms such as increased adiposity, glucose intolerance, dyslipidemia, and fatty liver. The treated mice also showed higher expressions of the genes related to mitochondrial energy metabolism (PPARγ coactivator-1α, nuclear respiratory factor-1) and caloric restriction (Sirt1) consistent with the increased mitochondrial biogenesis and energy expenditure.
CONCLUSIONS: Pharmacological activation of NADH oxidation by NQO1 resolves obesity and related phenotypes in mice, opening the possibility that it may provide the basis for a new therapy for the treatment of metabolic syndrome.
- Coenzyme+Q10+and+AMPK