DEFINITION
NGF (Nerve Growth Factor) is a 241 aa dimeric protein codified by a gene located on the 1p13.1 chromosome (The nerve growth factor: thirty-five years later, 1987). This gene is a member of the β-NGF family and encodes a secreted protein which homodimerizes and is incorporated into a larger complex. This protein has nerve growth stimulating activity and the complex is involved in the regulation of growth and the differentiation of sympathetic and sensory neurons.
THE GENE
Mutations in this gene have been associated with Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathy, type 5 (HSAN5), and dysregulation of this gene's expression is associated with Allergic Rhinitis (NGF nerve growth factor (beta polypeptide) [ Homo sapiens ], 2013).
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE AND IMAGES
When relevant for the function
- Primary structure
- Secondary structure
- Tertiary structure
- Quaternary structure
Protein Aminoacids Percentage


NGF has
- a low Glu/Gln ratio
- high arginine (high NO?)
- a relative abundance of all AA
SYNTHESIS AND TURNOVER
mRNA synthesis
protein synthesis
post-translational modifications

Which linkage between coagulation and NGF activation?
see
Plasmin digest a extracellular protein (Fibrin, NGF et ???) to make it more suitable as cell nutrient.
degradation
CELLULAR FUNCTIONS
cellular localization,
biological function

NGF works by binding to its high-affinity tyrosine kinase receptor, TrkA, found on the plasma membrane of these target cells. NGF binding causes TrkA receptors to dimerize and the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity of each receptor then phosphorylates its partner receptor. These phosphorylated tyrosines bind various adapter proteins or phospholipases (PLC), which, in turn, activate three major signaling pathways: the PI3kinase pathway leading to activation of Akt kinase, the ras pathway leading to MAP kinases, and the PLC pathway leading to release of intracellular Ca2+ and activation of PKC. The ras and PLC pathways primarily stimulate processes responsible for neuronal differentiation, while the PI3kinase pathway is primarily involved in cell survival.
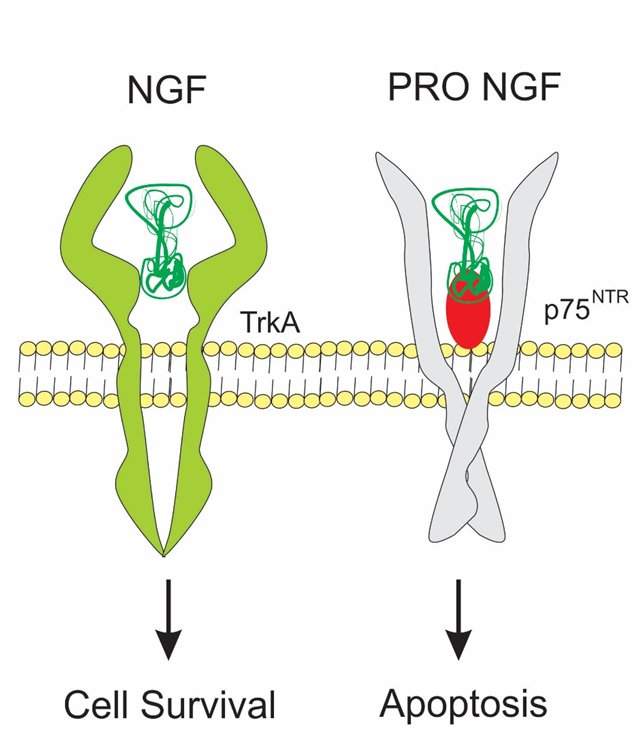
NGF receptors
Protein Aminoacids Percentage


NTRK1: survival ( higher level of Met His and Trp )
TNR16: apoptotic ( low methionine and Trp )

Ceramide analogues induce apoptosis in human cancer cells, and the inhibitor of acid ceramidase, an enzyme that promotes ceramide degradation, stimulates accumulation of ceramide, preventing tumor growth
- Cell signaling and Ligand transport
- Structural proteins
REGULATION
DIAGNOSTIC USE