s


Glutathione redox cycle. In the schematic diagram are represented the reduced (GSH) and oxidized forms (GSSG and GS-R) of glutathione. The reductionback of GSSG and GS-R by the action of GSSG reductase (GSSG-Red) and thioredoxin (Trx) are also shown together with the contribution of NADPH as upstreamsupplier of reducing equivalents. (GSH-Px ¼ Glutathione peroxidase)
Disulfide relays and phosphorylative cascades: Partners in redox-mediated signaling pathways, 2006

Redox modifications of reactive cysteine. Under physiological pH, a reactive cysteine can exist as thiolate anion, which more easily undergoes reversible oxidation either by the reaction with ROS ( S -hydroxylation) or by the reaction of the NO radical ( S -nitrosylation), or by the reaction with GSSG ( S -glutathiolation). The last modification could also be the result of reaction between sulfenic acid derivative of cysteine (-SOH) and GSH. This reaction has been suggested to represent a protection acted by GSH to preserve enzyme functionality from further oxidations, which can determine irreversible modifications of cysteine. In fact, besides the only peroxiredoxins I–III, which have been demonstrated to undergo reversible sulfinylation, no reduction to thiol form can be catalyzed for sulfinic (-SO 2 H) and sulfonic (-SO 3 H) acid derivatives

Modulation of thiol-dependent redox system by metal ions via thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems, 2018
- Abstract
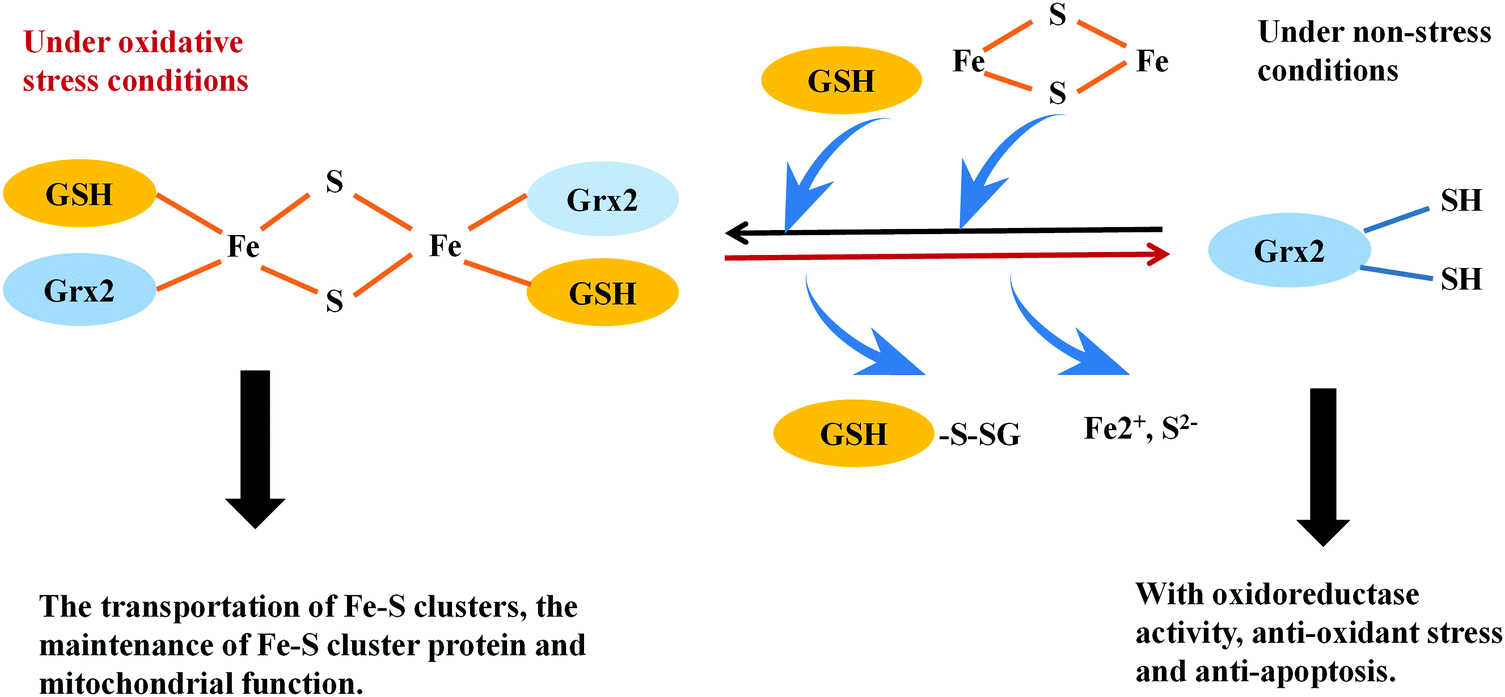
The thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems possess a variety of biological activities in mammalian cells, including the defense against oxidative stress, regulation of DNA synthesis, the cell cycle and the mediation of apoptosis. The thioredoxin system, comprised of NADPH, thioredoxin reductase (TrxR) and thioredoxin (Trx), exerts its activities via a disulfide–dithiol exchange reaction. Mammalian TrxRs are selenoproteins; the thiols and selenols in the active site of these enzymes confer the thioredoxin system to work as soft bases, which have a high affinity with soft acids, including numerous metal ions. In this review we focus on recent advances in the modulation of thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems by metal ion soft acids. Numerous clinical metal-containing drugs, such as platinum- and gold-containing compounds, show inhibitory effects on the thioredoxin system, providing strategies to develop novel anti-cancer drugs. Moreover, inhibition of the Trx system by soft acids, such as mercury-, chromium- and arsenic-containing compounds cause changes in the cellular redox state and contribute to their cell toxicity. In addition, metal ions are also involved in the regulation of the glutaredoxin system. Iron ions participate in regulating Grx2 activity via iron–sulfur cluster formation. Moreover, Grx5 in mitochondria contains a 2Fe–2S cluster stabilized by GSH, which can mediate cellular iron metabolism. Collectively, these results demonstrate that metal ions are major players in regulating the Trx and Grx systems-mediated cellular redox processes and thus, provide an opportunity to understand the functions of metal ions in thiol metabolism dysfunction-related diseases.
DEFINITION
A short protein description with the molecular wheight, isoforms, etc...
Use, when available, the link to Wikipedia (Es Trypsin)
External links not available on Wikipedia have to be added here
THE GENE
HGNC includes links to
- BioGPS
- GENATLAS
- GeneCards
- GOPubmed
- H-InvDB
- QuickGO
- Reactome
- Wikigenes includes links to
- NCBI
- NCBI SNP
- iHOP resource
- OMIM
- UniProt
- Ensembl
- HGNC
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE AND IMAGES
When relevant for the function
- Primary structure
- Secondary structure
- Tertiary structure
- Quaternary structure
Protein Aminoacids Percentage
The Protein Aminoacids Percentage gives useful information on the local environment and the metabolic status of the cell (starvation, lack of essential AA, hypoxia)
Protein Aminoacids Percentage (Width 700 px)

SYNTHESIS AND TURNOVER
mRNA synthesis
protein synthesis
post-translational modifications
degradation
CELLULAR FUNCTIONS
cellular localization,
biological function
- Cell signaling and Ligand transport
- Structural proteins
REGULATION
DIAGNOSTIC USE
Modulation of thiol-dependent redox system by metal ions via thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems 2018