Definition
Alzheimer Disease is the most common type of dementia. 
Alzheimer's is a degenerative and terminal disease for which there is no known cure. In its most common form, it afflicts individuals over 65 years old.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
age, sex, seasonality, etc
SYMPTOMS
DIAGNOSIS
NMR

Supplementary images
histopathology

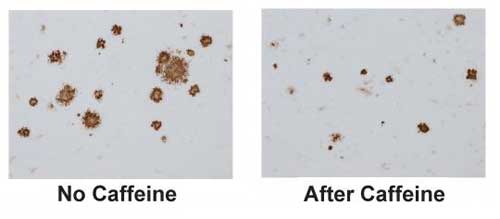
Caffeine?
The breakdown of glycogen in the lysosomes of newborn rat hepatocytes: the effects of glucose, cyclic 3',5'-AMP and caffeine. 1994
The effects of parenteral glucose, cyclic AMP and caffeine on the breakdown of glycogen in the lysosomes of newborn rat hepatocytes, were studied by using biochemical assays, electron microscopy and quantitative morphometry. Glucose prevented the normal postnatal increase in lysosomal volume, acid alpha 1,4 glucosidase activity and lysosomal glycogen breakdown. On the contrary, cyclic AMP and caffeine promoted this increase. There was a positive correlation between liver cyclic AMP concentration and acid glucosidase activity (R = 0.84, p < 0,001). Cyclic AMP also induced a change in the shape of lysosomes. The postulation that glucagon secreted after birth is the natural stimulus for the cyclic AMP-mediated postnatal increase in acid glucosidase activity and mobilization of the lysosomal glycogen in rat hepatocytes, is supported by these experimental findings.
radiology
NMR
laboratory tests
PATHOGENESIS
Amyloid plaque formation

Tutti sono capaci di farsi notare, ma per passare inosservati serve del talento vero.
Robert A. Heinlein

The neighborhood of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein
Alzheimer Disease Puglielli 2008
APP
gamma-Secretase
gamma-Secretase has different substrates


Loss-of-function presenilin mutations in Alzheimer disease. Talking Point on the role of presenilin mutations in Alzheimer disease 2007 B de Strooper

gamma-Secretase, notch, Abeta and alzheimer's disease: Where do the presenilins fit in? 2002






beta Amyloid and cholesterol

!!
PATIENT RISK FACTORS
Vascular
Genetic
A small percentage of patients have "familial Alzheimer's disease", which is caused by inherited changes in one of three proteins:
* Apolipoprotein E
* Amyloid precursor protein
* Presenilin 1 or 2
Apolipoprotein E is an important cholesterol carrying protein. It is found on the outer surface of low-density lipoproteins, or LDL, which are small particles that float in the blood plasma and carry cholesterol to cells that need it. The apolipoprotein E acts as a targeting protein. It binds to specific LDL receptors and the LDL particles are taken up into the cell, where the cholesterol is released. Although there are also apolipoprotein E receptors at the blood-brain barrier, LDL uptake into the brain from blood plasma is not a significant source of the brain's cholesterol. Most of the cholesterol in the brain is made by the brain cells as they need it, and any extra cholesterol in the brain is oxidized and rapidly removed.
Apolipoprotein E is associated with age-related risk for Alzheimer's disease and plays critical roles in Abeta homeostasis. We report that ApoE plays a role in facilitating the proteolytic clearance of soluble Abeta from the brain. The endolytic degradation of Abeta peptides within microglia by neprilysin and related enzymes is dramatically enhanced by ApoE. Similarly, Abeta degradation extracellularly by insulin-degrading enzyme is facilitated by ApoE. The capacity of ApoE to promote Abeta degradation is dependent upon the ApoE isoform and its lipidation status. The enhanced expression of lipidated ApoE, through the activation of liver X receptors, stimulates Abeta degradation. Indeed, aged Tg2576 mice treated with the LXR agonist GW3965 exhibited a dramatic reduction in brain Abeta load. GW3965 treatment also reversed contextual memory deficiency ApoE promotes the proteolytic degradation of Abeta. 2008
In this review, we re-examine a dangerous liaison between several viral and bacterial infections and the most significant genetic factor for AD, Infection and Alzheimer's disease: the APOE epsilon4 connection and lipid metabolism. 2008

more figures..
APOE and cholesterol metabolism


Increased CNV-Region deletions in mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer's disease (AD) subjects in the ADNI sample, 2013
Acquired
- High MCV depending on low B12 deficiency
Hormonal
Genetic
Acquired
Thyroid function, Alzheimer's disease and postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a tale of dangerous liaisons? 2008
Increasing evidence supports an extensive interrelationship between thyroid hormones and the cholinergic system, which is selectively and early affected in Alzheimer disease (AD).
Thyroid function in patients with Alzheimer disease: implications on response to anticholinesterase treatment. 2006
Thyroid hormones regulate beta-amyloid gene splicing and protein secretion in neuroblastoma cells. 1998
TISSUE SPECIFIC RISK FACTORS
anatomical (due its structure)
vascular (due to the local circulation)
The blood-brain barrier and microvascular water exchange in Alzheimer's disease. 2011
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia in the elderly. Although traditionally considered a disease of neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques, structural and functional changes in the microvessels may contribute directly to the pathogenesis of the disease. Since vascular dysfunction often precedes cognitive impairment, understanding the role of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in AD may be key to rational treatment of the disease. We propose that water regulation, a critical function of the BBB, is disturbed in AD and results in abnormal permeability and rates of water exchange across the vessel walls. In this paper, we describe some of the pathological events that may disturb microvascular water exchange in AD and examine the potential of a relatively new imaging technique, dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI, to quantify water exchange on a cellular level and thus serve as a probe of BBB integrity in AD.

Schematic diagram of the three-compartment model of tissue. EES: extravascular extracellular space; EIS: extravascular intracellular space; τb−1: unidirectional rate constant for water extravasation; Ktrans: pseudo-first-order rate constant for CR extravasation.

7T (a) DCE-MRI maps of blood volume (vb) and water permeability (PwS) in a superior slice from a 71-year-old female with early AD [78]. (b) T2-weighted spin echo image and corresponding pb map from a healthy 70-year-old female. Arrows indicate hyperintense white matter regions (15–23mm2) visible on both the T2 image and corresponding parametric map.
physiopathological (due to tissue function and activity)
COMPLICATIONS

Aspartic proteases inhibitors
 p=.
p=. 
The Notch signaling pathway plays an essential role in cell fate decisions during embryogenesis, hematopoiesis, and neuronal stem cell differentiation. Presenilins are required for the proteolytic release of the Notch-1 intracellular domain (NICD) from the cell membrane (14). After cleavage, the NICD translocates into the nucleus and acts as a transcription factor. The proteolytic release of NICD is reduced in PS1-deficient cells and abolished in PS1/PS2 double-knockout cells (30, 31). Reduction of Notch signaling is also observed in presenilin-deficient animal models.
Both APP and Notch proteolysis are blocked by presenilin-binding {gamma}-secretase inhibitors (41). Unfortunately, because both APP and Notch serve as substrates of {gamma}-secretase, inhibition of the protease as an AD therapy may interfere with Notch signaling in adults. Based on the known roles of Notch in adults, the most likely effect would be seen in hematopoiesis. Recent studies have shown that the treatment of fetal thymocyte cultures with {gamma}-secretase inhibitors interferes with T cell development in a manner consistent with the loss or reduction of Notch1 function (42, 43). Therefore, total inactivation of {gamma}-secretase will most likely be toxic.
h3. Related sites
Wurtman H
p25/cdk5 increases the amyloidogenic processing of APP through STAT3-mediated transcriptional control of BACE1 2008
Up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and altered cholesterol (CH) metabolism are characteristic of Alzheimer-diseased neural tissues. The liver X receptor (LXR) is a molecular sensor of CH homeostasis. In the current study, we determined the effects of HO-1 over-expression and its byproducts iron (Fe(2+)), carbon monoxide (CO) and bilirubin on CH biosynthesis, CH efflux and oxysterol formation in cultured astroglia. HO-1/LXR interactions were also investigated in the context of CH efflux. hHO-1 over-expression for 3 days ( approximately 2-3-fold increase) resulted in a 30% increase in CH biosynthesis and a two-fold rise in CH efflux.
Impact of heme oxygenase-1 on cholesterol synthesis, cholesterol efflux and oxysterol formation in cultured astroglia. 2009
Therapy
Therapeutic effects of remediating autophagy failure in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease by enhancing lysosomal proteolysis. 2011
Our findings underscore the pathogenic significance of autophagic-lysosomal dysfunction in AD and demonstrate the value of reversing this dysfunction as an innovative therapeautic strategy for AD.
Alzheimer: ruolo protettivo della memantina
Un approccio radiologico multimodale suggerisce che la memantina possa avere effetti benefici nei pazienti con forme lievi-moderate di morbo di Alzheimer. Si tratta del primo studio che abbia utilizzato la neuroradiologia multimodale per esplorare i possibili effetti terapeutici della memantina su metabolismo, funzionalità e morfologia del cervello. La memantina si è dimostrata in grado di rallentare il declino nel metabolismo del glucosio in ogni area cerebrale, nonché anche la progressione dell'atrofia ippocampale. Si tratta di un effetto in grado di modificare il decorso della malattia, che andrà confermato in studi più ampi che comprendano l'uso della PET e di parametri di funzionalità dell'ippocampo. (J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2008; 79: 1312-7)
Meno demenza con livelli elevati di leptina
In pazienti anziani, i livelli plasmatici di leptina risulterebbero correlati all'incidenza di demenza e morbo di Alzheimer, oltre che al volume cerebrale. Questi i risultati di uno studio, pubblicato su Jama, che è stato ideato alla luce del riscontro di effetti benefici di tale ormone sulla plasticità sinaptica dell'ippocampo, sulla rimozione delle placche beta-amiloidi e sulle capacità mnemoniche in modelli animali d'invecchiamento e Alzheimer. Tra il 1999 e il 2005, circa 200 individui senza problemi cognitivi sono stati sottoposti a misurazioni del volume cerebrale attraverso analisi di risonanza magnetica nucleare. Dopo un follow-up medio di 8,3 anni, 111 partecipanti hanno sviluppato demenza e 89 Alzheimer. Modelli di analisi multivariata hanno consentito di stabilire una chiara associazione tra livelli elevati di leptina e diminuzione del rischio di demenza e Alzheimer (hazard ratio= 0,68 e 0,60, rispettivamente). In conclusione, dopo 12 anni, il 25% dei soggetti con leptina bassa si ammalerebbe di Alzheimer, contro il 6% di quelli con tassi elevati. In aggiunta, alte concentrazioni plasmatiche dell'ormone sono apparse associate a un maggiore volume cerebrale totale. (L.A.)
Jama 2009;302(23):2565-2572
MGAT3 mRNA: a biomarker for prognosis and therapy of Alzheimer's disease by vitamin D and curcuminoids. 2011