Sphingomyelin is a major component of animal plasma membranes.
Sphingomyelin synthesis from Ceramide and Phosphatidylcholine is catalized by Sphingomyelin synthase in a reaction also yielding diacylglycerol as a side product.
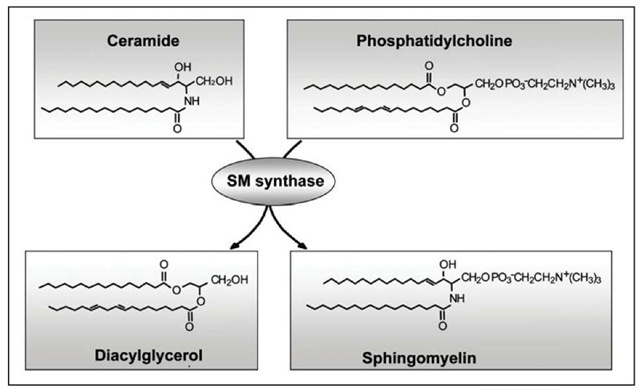
SM synthase decreases ceramide a proapoptotic stimulus and increases diacylglycerol an antiapoptotic stimulus.
Sphingomyelin synthases localization
SM synthesis occurs in the lumen of the Golgi as well as on the cell surface.
Human, mouse and Caenorhabditis elegans genomes each contain at least two different SM synthase (SMS) genes. Whereas human SMS1 is localised to the Golgi, SMS2 resides primarily at the plasma membrane.
Identification of a family of animal sphingomyelin synthases 2004
THE GENES

This reaction is catalysed by SM synthase, an enzyme whose biological potential can be judged from the roles of diacylglycerol and ceramide as anti- and proapoptotic stimuli, respectively. SM synthesis occurs in the lumen of the Golgi as well as on the cell surface. As no gene for SM synthase has been cloned so far, it is unclear whether different enzymes are present at these locations. Using a functional cloning strategy in yeast, we identified a novel family of integral membrane proteins exhibiting all enzymatic features previously attributed to animal SM synthase. Strikingly, human, mouse and Caenorhabditis elegans genomes each contain at least two different SM synthase (SMS) genes. Whereas human SMS1 is localised to the Golgi, SMS2 resides primarily at the plasma membrane. Collectively, these findings open up important new avenues for studying sphingolipid function in animals.