.

Topology of membrane proteins
Intrinsic Proteins
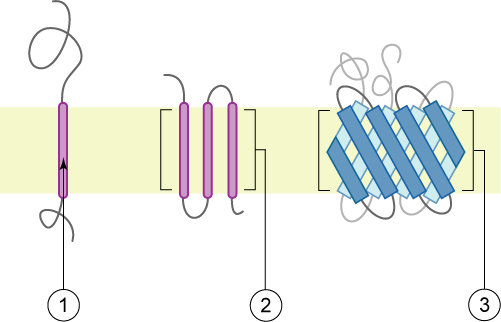
A transmembrane protein is a protein that spans the entire biological membrane. Transmembrane proteins aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents.
Membrane Protein Inserption

GPI-anchored Proteins

- The relationship between the structures and functions of the GPI anchor is difficult to study due to the lack of sufficient quantities of pure anchors and anchored proteins. When produced in cells, GPI-anchored proteins exist as heterogeneous mixtures with considerable variation in their glycan core modifications and lipid moieties, a complicating feature with respect to functional analysis (1, 13, 18, 58). Furthermore, well-defined modifications to the GPI anchor structure cannot be imposed using conventional biological methods; the biosynthetic enzymes are not well characterized, and their disruption in cells simply leads to loss of the entire GPI structure.
The GPI-anchor and protein sorting 2001


- The GPI anchor is a structurally complex posttranslational modification that remains a mystery with respect to its biological activities.
- Protein Moiety
- PrP

Table 1. Functional diversity of GPI-anchored proteins.
- Enzymes Surface antigens
- Acetylcholinesterase Thy-1, Ly-6 (TAP), Qa-2,
- alkalinephosphatase, 5¢- Sca-2, CD24, CD48 (sgp-60),
- nucleotidase, dipeptidase, CD52 (CAMPATH-1), CD-5
- lipoprotein lipase, ART1 (DAF), CD59, CD73,
- ART2 (RT6) cerebroglycan,
- Adhesion molecules
- ceruloplasmin, prion proteins
- NCAM, ApCAM, OBCAM Other (lower eukaryotes)
- F3/F11/contain), TAG-
- Variant surface glycoprotein
- 1 (axonin-1), fasciclin II, (VSG), SSp-4, sialic acid
- BIG-1, BIG-2, neurotrimin, acceptor, 160-kDa flagellar
- LFA-3 antigen, CS protein, MSP-1
- Receptors
- protease, MSP-2, MSP-4,
- Folate receptor, CNTFR-a gp63 metalloprotease, PSA-2,
- GDNFR-a, CD87 (uPAR) PARP/procyclin,
- NTNR-a, CD14, glypicans GP-2
FcgRIIIb,
The Glycosylphosphatidylinositol Anchor: A Complex Membrane-Anchoring Structure for Proteins 2008
Table 2: Representative Functions of GPI-Anchored Proteins (2, 3, 17, 27)
biological role
protein
source
enzymes
alkaline phosphatase
mammalian tissues, Schistosoma
5′-nucleotidase
mammalian tissues
acetylcholinesterase
Torpedo electric organ, insect brain, mammalian blood cells
dipeptidase
pig and human kidney, sheep lung
cell−cell interaction
LFA-3
human blood cells
NCAM
mammalian and chicken brain and muscle
PH-20
guinea pig sperm
complement regulation
CD55 (DAF)
human blood cells
CD59
human blood cells
mammalian antigens
Thy-1
mammalian brain and lymphocytes
Qa-2
mouse lymphocytes
CD14
human monocytes
carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
human tumor cells
CD52
human lymphocytes
protozoan antigens
VSG
T. brucei
1G7
T. cruzi
procyclin
T. brucei
miscellaneous
scrapie prion protein
hamster brain
CD16b
human neutrophils
folate-binding protein
human epithelial cells
Differential sorting and fate of endocytosed GPI-anchored proteins 2002