DESCRIPTION
Trifolium pratense , also called Red Clover, is a species of clover, a wild plant belonging to the legume family. Red clover is a perennial herb that commonly grows wild in meadows throughout Europe, Western Asia and Northwester Africa and has now been naturalized to grow in North America. It is an herbaceous, variable in size, growing to 20–80 cm tall. The flowers are dark pink produced in a dense inflorescence.

COMPOSITION
Red clover is a source of many nutrients: Calcium, Chromium,Magnesium, Niacin, Phosphorus, Potassium, Thiamine, Vitamin C.
PROPERTIES AND USES
It has been used medicinally to treat a number of conditions. Traditionally, these have included cancer, whooping cough, respiratory problems, and skin inflammations, such as psoriasis and eczema. Red clover was thought to "purify" the blood by acting as a diuretic by helping the body get rid of excess fluid, and expectorant by helping clear lungs of mucous, improving circulation, and helping cleanse the liver. Red clover’ s flowers contain flavones derivated from coumarin. A type of flavones are isoflavones (estrogen-like compounds) which can mimic the effect of endogenous estrogen. Among flavonoides there are isoflavones , natural fitoestrogenes with antioxidan effects.
Clinical evidence is lacking to support the efficacy of semipurified red clover isoflavone extracts for alleviation of climacteric vasomotor symptoms or reduction of low-density lipoprotein levels in the blood. Limited evidence suggests possible efficacy in maintenance of bone health and improvement of arterial compliance, a risk factor for atherosclerosis.
Clinical studies of red clover (Trifolium pratense) dietary supplements in menopause: a literature review, 2006
In red clover are contained four types of isoflanoides : genistein ( isolated from broom in 1899) daidzein, formononetin e biochanin A (genistein’s precursor).

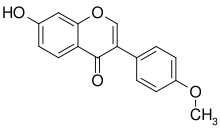 Formononetin
Formononetin
These substances bind estrogenes’ receptors . These are intracellular receptors , there are two different isoforms ER alfa and Beta costituited by five domaines. A/B domain with amino terminal region and Af 1 region , C domain ( DNA binding domain ), D domain with nuclear localization signal NLS , E domain( ligand binding domain), F domain carbossi terminal. When estrogenes bind receptor this halves and moves to the nucleus from cytoplasm , and here binds on Dna “estrogen response elements” (ERE), causing genomic effects.
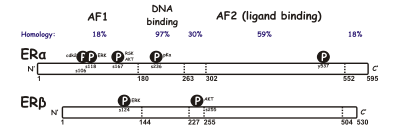
The domain structures of ERα and ERβ, including some of the known phosphorylation sites involved in ligand-independent regulation.
TRIFOLIUM PRATENSE: A BODYGUARD AGAINST TUMORS
Red clover contrast prostate tumor, endometrial, breast and colon cancer . In particular Ginestein has an elevated antioxidant power against development of tumors .
Genistein and other isoflavones have been identified as angiogenesis inhibitors and found to inhibit the uncontrolled cell growth of cancer, most likely by inhibiting the activity of substances in the body that regulate cell division and cell survival. It has also been shown that genistein makes some cells more sensitive to radio-therapy. Genistein's chief method of activity is as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Tyrosine kinases are less widespread than their ser/thr counterparts but implicated in almost all cell growth and proliferation signal cascades. Inhibition of DNA topoisomerase II also plays an important role in the cytotoxic activity of genistein. Due to its structure similarity to 17β-estradiol(estrogen), genistein can compete with it and bind to estrogen receptors. However, genistein shows much higher affinity toward estrogen receptor β than toward estrogen receptor α. Data from in vitro and in vivo research confirms that genistein can increase rate of growth of some ER expressing breast cancers. Genistein was found to increase the rate of proliferation of estrogen-dependent breast cancer when not co-treated with an estrogen antagonist. It was also found to decrease efficiency of tamoxifen and letrozole - drugs commonly used in breast cancer therapy. Therefore isoflavones were tested for their effect on cell proliferation, apoptosis induction and cell cycle arrest. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting was used to detect the induction of apoptosis or cell cycle arrest. Isoflavones and plant extracts significantly reduced the proliferation activity of the treated cancer cell lines.
Effects of red clover extracts on breast cancer cell migration and invasion., 2012
TRIFOLIUM PRATENSE AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTION
Red clover protects from cardiovascular and dismetabolic diseases . Red clover isoflavones have been associated with an increase in "good" HDL cholesterol in pre and postmenopausal women. Furthermore Genistein is able to inhibit the oxidation of LDL in the presence of copper ions or superoxide/nitric oxide radicals alteration in electrophoretic mobility, and lipid hydroperoxides. Human endothelial cell-mediated LDL oxidation is also inhibited in the presence of genistein. The 7-O-glucoside of genistein, genistin, is much less effective in inhibiting LDL oxidation in the cell-free and cell-mediated lipoprotein-oxidating systems. Incubating human endothelial cells in the absence or presence of genistein and challenging the cells with already oxidized lipoprotein reveals that in addition to its antioxidative potential during LDL oxidating processes, genistein effectively protects the vascular cells from damage by oxidized lipoproteins. The tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein was found to block upregulation of two tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins in endothelial cells induced by oxidized LDL. One study found that menopausal women taking red clover supplements had stronger, more flexible arteries with enlarged compliance ,which can help prevent heart disease. Red clover may also have blood thinning properties, which keeps blood clots from forming.
Effects of estrogen on the vascular system,2003
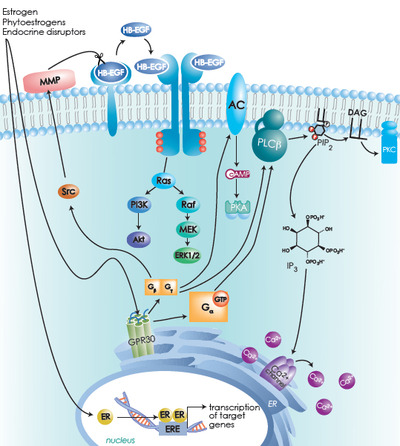
Intracellular estrogens-phytoestrogen segnaling cascades initiated trought both the classical nuclear receptor Er
TRIFOLIUM PRATENSE AND HIS USE TO FIGHT OSTEOPOROSIS
An important effect of this plant is protection from osteoporosisby increasing bone mineralization. As estrogen levels drop during menopause, a woman's risk for developing osteoporosis ,significant bone loss, goes up. A few studies suggest that a proprietary extract of red clover isoflavones may slow bone loss and even boost bone mineral density in pre and perimenopausal women. Biochanin A , contained in red clover , causes a significant elevation of cell growth, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, collagen content, and osteocalcin secretion in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells of mouse. Moreover the treatment with isoflavones significantly reduced the number of osteoclasts compared with the ovariectomized control rats.
Effects of phytoestrogenic isoflavones from red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) on experimental osteoporosis,2007
TRIFOLIUM PRATENSE: A NATURAL ALLIED DURIN MENOPAUSE ?
Red clover can be used to treat the symptoms of menopause. Traditionally, red clover has been administered to help restore irregular menses and to balance the acid-alkaline level of the vagina to promote conception. In a clinical study, researchers concluded that a diet supplemented with red clover sprouts and other plants that contain phytoestrogens may reduce the severity of menopausal symptoms. Compared with placebo, red clover isoflavone supplementation in postmenopausal women significantly decreased menopausal symptoms and had a positive effect on vaginal cytology and triglyceride levels. However, this needs to be confirmed in other studies before red clover can be routinely recommended.
The effect of red clover isoflavones on menopausal symptoms, lipids and vaginal cytology in menopausal women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study,2005
ADMINISTRATION and controindications
Red clover is available in a variety of preparations, including teas, tinctures, tablets, capsules, liquid extrac. It can also be prepared as an ointment for topical -skin application. Due to its coumarin derivatives, it should be used cautiously in individuals with coagulation disorders or currently undergoing anticoagulation therapy. It is metabolized by CYP3A4 and therefore caution should be used when taking it with other drugs using this metabolic pathway.
No serious side effects have been reported in people taking red clover for up to one year. General side effects m