DEFINITION
Juvenile hemochromatosis (JH), also classified as type 2, is a rare autosomal recessive disorder of iron overload that leads to organ damage before the age of 30. JH is usually associated with liver cirrhosis, cardiomyopathy and/or hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism, that is the main symptom at disease presentation, and the course of symptoms is more rapid and severe than classic HFE hemochromatosis (type 1). Men and women are equally affected. Typically, patients with JH die prematurely of cardiovascular causes before reaching their fourth decade of life.
Cases of non-HFE hemochromatosis due to HJV (hemojuvelin) or HAMP mutations are denominated type 2 HH; those related to TFR2 (receptor 2 of transferrin) mutations are named type 3 HH; and cases associated with SLC40A1 mutations, which can be significantly different from classic cases of HH, receive the denomination of type 4 HH or "ferroportin disease".
Se ci sono più voci su OMIM usare questo formato di ricerca:
 Autism
Autism
TYPE OF HEMOCHROMATOSIS
1)Type 1
-transmission:recessive
-gene involved:HFE
-age of onset:40-50
-target organs:heart,liver,pancreas,joints,gonads
2)Type 2
-transmission:recessive
-gene involved:HJV and HAMP
-age of onset:10-20
-target organs:heart,gonads,liver,pancreas,joints
3)Type 3
-transmission:recessive
-gene involved:TFR2
-age of onset:30-40
-target organs:liver,joints,pancreas,heart,gonads
4)Type 4
-transmission:dominant
-gene involved:Ferroportin
-age of onset:40-50
-target organs:liver,joints,pancreas,heart,gonads
Juvenile hemochromatosis
Non-HFE hemochromatosis
ROLE OF HEMOJUVELIN IN THE IRON METABOLISM
Iron absorption occurs in the duodenum and is influenced by quantity and bioavailability of iron in the diet,organic deposits of iron (in hepatocytes, linked to ferririna), speed of erythropoiesis and hypoxia of tissues.
Specialized cells in the release of iron are enterocytes and macrophages that receive ferroportin on their basolateral membrane. It is the only carrier dedicated to iron export.
Its interaction with hepcidin (peptide secreted by the liver in response to iron and inflammation) blocks iron export.
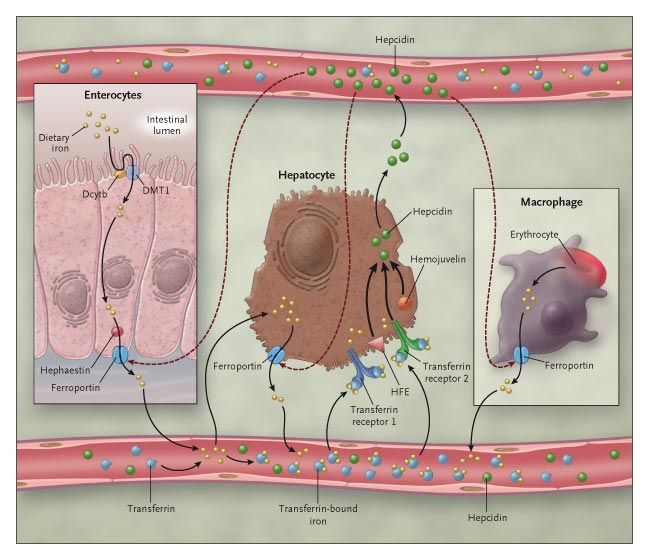
Hemojuvenil is a transcriptional regulator of hepcidin and its interaction with BMP (Bone Morphogenetic Protein) -BMP receptors complex activates SMAD. Phosphorylated SMAD 1/5/8 forms heteromeric complexes with SMAD4 and translocates to the nucleus to activate the target HAMP gene promoter.

Hemojuvelin is transcribed from a gene of 4265 bp (constituted by four exons and located in chromosome 1) into a full length transcript with five spliced isoforms. Analyses of hemojuvelin in human tissues detect substantial expression in adult and fetal liver, heart, and skeletal muscle.The putative full length protein is 425 aminoacids with a large RGM motif,( homologous to repulsive guidance molecules) divided into two portions: N-terminal ( two domains GRP and RGD) and C-terminal characterized by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linked membrane anchor ( GPI anchor ) and homologous to that constituted by the vWF.
HJV is identical to RGMc, which with RGMa and RGMb comprise the repulsive guidance molecule (RGM) family. RGMc is produced in the liver and striated muscle, whereas RGMa and RGMb are primarily synthesized in the central nervous system, where they are involved in regulating neuronal survival and axonal patterning during development. RGM family members are glycoproteins that share several structural motifs, and all three can undergo a series of similar biosynthetic and processing steps leading to cell-associated glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked and soluble protein species.
The precise biological roles for each RGMc species in systemic iron balance also have not been defined yet. Recent studies have hypothesized that cell-associated RGMc functions as a co-receptor for selected BMP, and can facilitate the ability of BMPs to stimulate hepcidin gene expression in the liver.
Soluble Repulsive Guidance Molecule c/Hemojuvelin Is a Broad Spectrum Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) Antagonist and Inhibits both BMP2- and BMP6-mediated Signaling and Gene Expression

Under the influence of different proteolytic activities, soluble forms of hemojuvelin are generated (sHJV, sHJV’). Furin-like proprotein convertase, stimulated by hypoxia and iron deficiency, cleaves HJV to release a form of sHJV that can sequester BMP, thereby inhibiting the signal transduction by decreasing the effective concentrations of BMP and membrane HJV. Matriptase 2 (MT2) binds and cleaves cell surface HJV, decreasing the association of cell surface HJV with the BMPR complex, and thereby decreasing signaling. The small sHJV isoform generated by MT2, sHJV’, may not sequester BMP. However, the physiological role of these soluble products remains uncertain.
CONCLUSION
HFE testing for the two main mutations (p.Cys282Tyr and p.His63Asp) should be performed in all suspected patients with primary iron overload and unexplained increased transferrin and/or serum ferritin values. The evaluation of the HJV p.Gly320Val mutation must be the molecular test of choice in suspected patients with juvenile hemochromatosis.
Molecular Diagnostic and Pathogenesis of Hereditary Hemochromatosis