DEFINITION
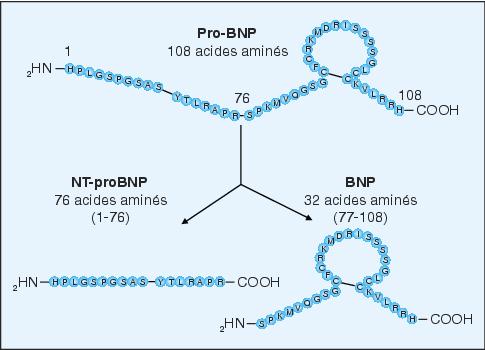
Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), , is a 32-amino acid polypeptide secreted by the ventricles of the heart in response to excessive stretching of heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes). The release of BNP is modulated by calcium ions. BNP is named as such because it was originally identified in extracts of porcine brain, although in humans it is produced mainly in the cardiac ventricles.
The N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide is a 76 amino acid N-terminal inactive protein that is cleaved from proBNP to release brain natriuretic peptide.
Both BNP and NT-proBNP levels in the blood are used for screening, diagnosis of acute congestive heart failure (CHF) and may be useful to establish prognosis in heart failure, as both markers are typically higher in patients with worse outcome.

The Ability of Heart Failure Specialists to Accurately Predict NT-proBNP Levels Based on Clinical Assessment and a Previous NT-proBNP Measurement, 2008
The value of routine aminoterminal pro type B natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) measurements in outpatient clinics remains unknown.
Objectives:
We sought to determine the accuracy with which heart failure (HF) specialists can predict NT-proBNP levels in HF outpatients based on clinical assessment.
Methods:
We prospectively studied 160 consecutive HF patients followed in an outpatient multidisciplinary HF clinic. During a regular office visit, HF specialists were asked to estimate a patient’s current NT-proBNP level based upon their clinical assessment and all available information from their chart, including a previous NT-proBNP level (if available). NT-proBNP estimations were grouped into prognostic categories (<125, 125-1000, 1000-4998, or ≥4999 pg/mL) and comparisons made between actual and estimate values.
Results:
Overall, HF specialists estimated 67.5% of NT-proBNP levels correctly. After adjusting for clinical characteristics, knowledge of a prior NT-proBNP measurement was the only significant predictor of estimation accuracy (p=0.01). Compared to patients with a prior NT-proBNP level <125 pg/mL, physicians were 95% less likely to get a correct estimation in patients with the highest prior NT-proBNP level (≥4999 pg/mL).
Conclusion:
HF specialists are reasonably accurate at estimating current NT-proBNP levels based upon clinical assessment and a previous NT-proBNP level, if those levels were < 4999 pg/mL. Likely, initial but not routine NT-proBNP measurements are useful in outpatient HF clinics.
| Database | Link |
| "XYZZ": | "test": |
| "ZXVX": | "URL": |
ANALYTICAL METHOD
ANALYTICAL TRICKS AND TIPS
THE BIOLOGICAL CONTEXT
NT-proBNP+kidney+blood+flow

!{width:56px;height:20px}http://flipper.diff.org/static/files/1011/Quertle-70.gif!NT-proBNP kidney blood flow
Biological actions of brain natriuretic peptide in thoracic inferior vena caval constriction. 1993
In normal dogs BNP increased glomerular filtration rate, renal blood flow, and urinary sodium excretion and decreased proximal and distal fractional reabsorption of sodium with activation of urinary guanosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate (cGMP).
h3. DIAGNOSTIC USE
Issues

The causes and mechanisms of elevated natriuretic peptides levels. *The main reason of elevated natriuretic peptides and the best-established use of these testing. Circumstances in the example list may share more than one mechanism.
Specificity, sensitivity etc.
Diagnostic and prognostic values of B-type natriuretic peptides (BNp) and N-terminal fragment brain natriuretic peptides (NT-pro-BNp), 2013
B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a member of a four-natriuretic peptide family that shares a common 17-peptide ring structure. The N-terminal fragment (NT-pro-BNP) is biologically inert, but both are secreted in the plasma in equimolar quantities and both have been evaluated for use in the management of congestive heart failure. BNP and NT-pro-BNP are frequently used in the diagnosis of congestive heart failure and distinguishing between patients with dyspnoea of cardiac or pulmonary origin. Values of NT-pro-BNP are affected by age or the presence of one or several co-morbidities such as chronic renal failure, type 2 diabetes, and acute coronary syndrome. ‘Normal’ values of these peptides also vary depending on the type of test used. The performance characteristics of these tests vary depending on the patients on whom they are used and the manufacturer. For this reason, the determination of reference values for this peptide represents such a challenge.
Diagnostic Algorithms

PROs and CONTROs
h4. Kidney Diseases
Google nt-probnp kidney
Open Questions
Working Hypothesis