Overview of the structure of neurofilaments and neurofilament light chain. Large calibre myelinated axons abundantly express neurofilaments (Nfs). Nfs are cylindrical structures of 10 nm calibre and they are exclusively located in neurons. They confer structural stability to the axons, enable the radial growth of the myelinated axons and expand their calibre thus allowing a higher conduction velocity.

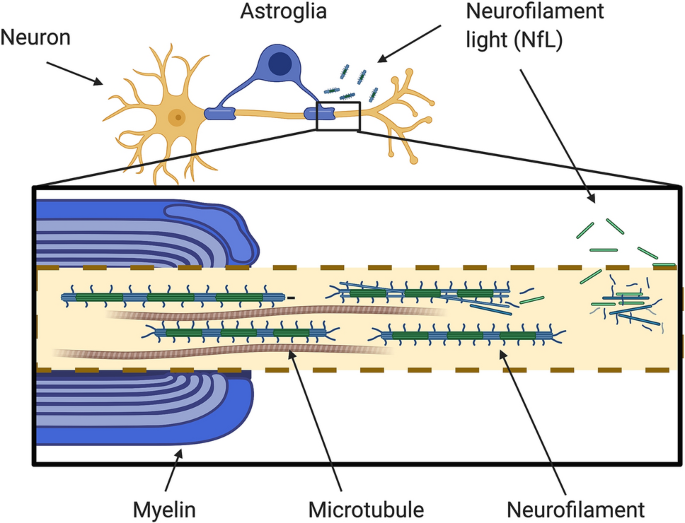
Nfs are classified as intermediate filaments (IF), that is, as filaments with an intermediate diameter (10 nm) between actin (6 nm) and myosin (15 nm). In the central nervous system (CNS), Nfs are made of neurofilament light chain (NfL), neurofilament middle chain (NfM), neurofilament heavy chain (NfH) and α-internexin (α-int). All of these subunits have a conserved α-helical rod domain with a variable amino-terminal and carboxy-terminal region. The length of these latter confers a different molecular weight. NfH has the highest molecular weight and presents, in its tail, a glutamic-acid-rich segment (E segment), multiple lysine-serine-proline (KSP) repeats that are phosphorylated and a lysine-glutamic acid-proline (KEP) segment. NfM has a shorter tail with two glutamic-acid-rich segments (E1 and E2 segments), two KSP repeat segments and a serine-proline (SP) and lysine-glutamic acid (KE) segment. The tail of NfL is made of the glutamic-acid-rich segment (E segment). Finally, α-int has, in its tail, an E segment and a KE
Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders, 2018
DEFINITION
A short protein description with the molecular weight, isoforms, etc...
Use, when available, the link to Wikipedia (Es Trypsin)
External links not available on Wikipedia have to be added here
THE GENE
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE AND IMAGES
When relevant for the function
- Primary structure
- Secondary structure
- Tertiary structure
- Quaternary structure
Protein Aminoacids Percentage (Width 700 px)


SYNTHESIS AND TURNOVER
mRNA synthesis
protein synthesis
post-translational modifications
degradation
CELLULAR FUNCTIONS
cellular localization,
biological function
- Cell signaling and Ligand transport
- Structural proteins
REGULATION
DIAGNOSTIC USE