Cytoplasmic Calcium Regulation


Dose dependence of oscillations frequency (vasopressin, histamine etc)

Metabolic oscillation at cellular level
 .
.
Metabolic oscillation
Glucose and Insulin

Circadian rhythm (cortisol)


from Complementary Oncology

NOCTURNIN expression profiles calculated in lymphocytes from 15 healthy volunteers collected at 4-hour intervals over 24 h. NOCTURNIN mRNA levels are expressed as geometric mean ± 95% confidence interval. A significant diurnal variation was highlighted by repeated measures ANOVA and Cosinor analysis.∗ p < 0.05 compared to nearest times.
Urinary flow circadian rythm

Cortisol endothelin-1 circadian rhythm

Circadian glucocorticoid oscillations promote learning-dependent synapse formation and maintenance, 2013

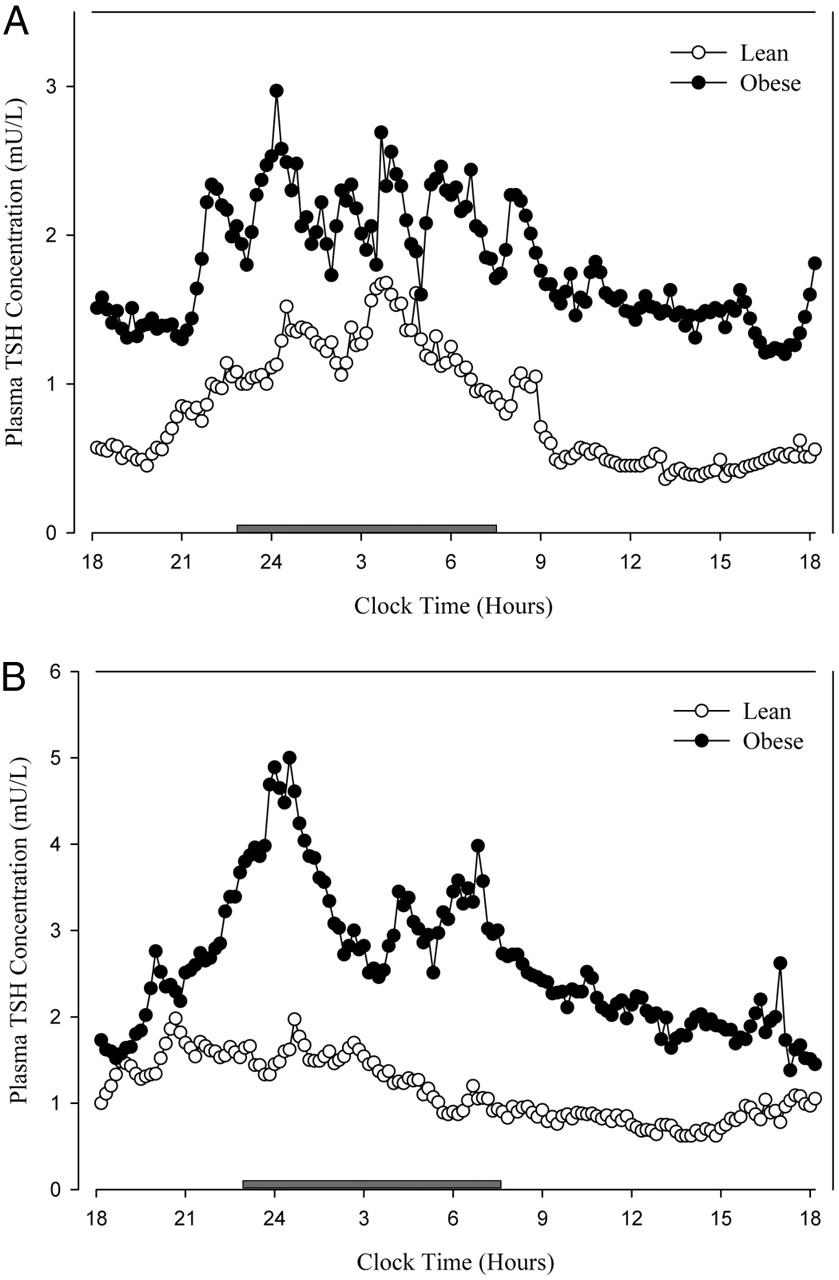
Circadian rhythm (TSH)


√, 2012
h3. Circadian rhythm
In fact, TSH is one of the well-known hormones, such as cortisol, melatonin, prolactin, etc. that change as part of the daily circadian rhythm. TSH peaks during the night and remains lower during the day. The fact that serum T4 and T3 levels remain relatively constant despite this change is intriguing, though again, there is likely a good deal of regulation we don't understand and that is difficult to measure at an intracellular level, and it may have to do with some of the regulation I talk about in a couple of paragraphs.

The effects of photoperiod on growth rate and circulating thyroid hormone levels in the red drum, Sciaenops ocellatus: evidence for a free-running circadian rhythm of T4 secretion, 2001


Chronobiology in the endocrine system, 2007

Circadian rhythm in the number of vasopressin-containing neurons in the human suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of *(A) young subjects (<50 years of age)* and *(B) elderly subjects (>50 years of age)*. The black bars indicate the night period (22:00–06:00 h). The general trend in the data is enhanced by using a smoothed double plotted curve and is represented by mean ±SEM values. Note the circadian rhythm in the SCN of young people, with low values during the night period and peak values during the early morning.
Hypothalamic Peptides in Human Brain Diseases, 1999
CSF Na+ Rhythm


Cerebrospinal fluid sodium rhythms, 2010
Link to Migraine??
Hearthbeat fractal behaviour

Nonlinear Dynamics, Fractals, and Chaos Theory:
Implications for Neuroautonomic Heart Rate Control
in Health and Disease
Heart diseases circadian rate

Circadian rythm in sheep
Clock genes

High-Fat Diet Disrupts Behavioral and Molecular Circadian Rhythms in Mice, 2007