Il Glutatione (GSH) è un tripeptide formato da glutamato, cisteina e glicina. La presenza del gruppo -SH gli permette sia di funzionare da anti-ossidante che da legante di numerose sostanze che, una volta coniugate con il GSH, vengono escrete.

Video Sul Glutatione 20 aprile 2022. (La mia parte inizia al minuto 22), organizzato dalla SIM
Testo preliminare sul GSH
Decadimento con l'età
Per comprendere appieno il significato biologico del GSH, non basta elencare le reazioni a cui prende parte, ma comprendere quale è l'ambiente che ne rende possibile la sintesi.

Il contenuto di informazione di ogni molecola del nostro organismo comprende anche la sommatoria di tutte le condizioni che ne rendono possibile la sintesi
Nel caso del GSH le condizioni sono:
La disponibilità nelle cellule di:
La disponibilità nel siero di:
- glutamato (0.041/0.067, Glu+Gln 0.65/0.56)
- cisteina (0.002/0.016)
- glicina (0.244/0.315)
(Serum amino acid concentrations in aging men and women, 2003)
Le proprietà degli enzimi coinvolti
- glutamato-cisteina ligasi (GCL): km ATP : 0.26 - 4.47, glutamate: 0.7/3.5, cysteine: 0.1 - 0.8
- glutatione sintasi (GS). km ATP: 0.02/2.66 gamma-L-Glu-L-Cys: 0.34/0.66, Glicina: 0.36/2.52

Cellular GSH homeostasis and GSH-dependent reactions. Intracellular GSH balance is maintained by de novo synthesis, regeneration from GSSG, and extracellular GSH uptake. In transport epithelial cells, such as enterocytes, γ -glutamyl transferase ( γ -GT) and dipeptidase (DP) catalyzed the hydrolysis of extracellular GSH to its constituent amino acids, glutamate, cysteine and glycine. Additionally, intestinal epithelial cells can import intact GSH from the lumen via specifi c plasma membrane transporters. Cytosolic synthesis of GSH takes place in two ATP-dependent reactions catalyzed by glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL) and glutathione synthase (GS). The intracellular GSH pool, present in millimolar concentrations, is involved in various GSH-dependent reactions. Compartmentation of GSH within the mitochondria, nucleus or endoplasmic reticulum creates distinct and independently regulated subcellular redox pools. As part of the antioxidant defence system, GSH participates in conjugation reactions catalyzed by glutathione-S-transferases (GSTs), in the reduction of hydrogen peroxide (H O ) and lipid hydroperoxides (LOOH) catalyzed by glutathione peroxidases (Gpxs), and the reduction 2 2 of protein-disulfi des (PrSSG) catalyzed by glutaredoxins (Grxs). The reduction of glutathione disulfi de (GSSG) by glutathione reductase (GR) in the GSH redox cycle regenerates GSH. GSSG reduction occurs at the expense of NADPH, produced from the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) from glucose oxidation.
GSH synthesis regulation
Regulation of glutathione synthesis, 2008(GCL).
- Glutathione (GSH) is a ubiquitous intracellular peptide with diverse functions that include detoxification, antioxidant defense, maintenance of thiol status, and modulation of cell proliferation. GSH is synthesized in the cytosol of all mammalian cells in a tightly regulated manner. The major determinants of GSH synthesis are the availability of cysteine, the sulfur amino acid precursor, and the activity of the rate-limiting enzyme, glutamate cysteine ligase (GCL). GCL is composed for a catalytic (GCLC) and modifier (GCLM) subunit and they are regulated at multiple levels and at times differentially. The second enzyme of GSH synthesis, GSH synthase (GS) is also regulated in a coordinated manner as GCL subunits and its up-regulation can further enhance the capacity of the cell to synthesize GSH. Oxidative stress is well known to induce the expression of GSH synthetic enzymes. Key transcription factors identified thus far include Nrf2/Nrf1 via the antioxidant response element (ARE), activator protein-1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB). Dysregulation of GSH synthesis is increasingly being recognized as contributing to the pathogenesis of many pathological conditions. These include diabetes mellitus, pulmonary fibrosis, cholestatic liver injury, endotoxemia and drug-resistant tumor cells. Manipulation of the GSH synthetic capacity is an important target in the treatment of many of these disorders.
Dimorfismo sessuale
Sexual_dimorphism_in_glutathione_metabolism, 2020
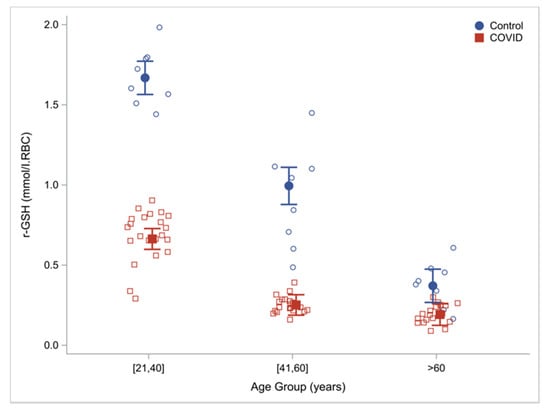
GSH e COVID-19
The Role of Glutathione in Protecting Against the Severe Inflammatory Response Triggered by COVID-19, 2020: Scite