Introduction

Diospyros kaki (commonly called khaki or khaki persimmon, or even diospyro) is a fruit tree native of Eastern countries, belonging to the family of Ebenacee (the same of ebony). Among the various nicknames by which it is remembered, can not miss "Apple of the East" and "lotus of Japan".
The persimmon is known in botany as Diospyros kaki: the term derives from the greek and is constituted by a combination of two words, "Diòs" (referring to the god Jupiter) and "pyròs" (wheat); literally, then, the persimmon is defined the wheat of Jupiter.
In China, legend has it that the plant persimmon tree, embodies the seven virtues, referring essentially to the sweetness of the fruits, the sturdy wood, the longevity of the plant, the decorative use of its leaves, the fire produced by the ardor of its branches, the possibility given to the birds of building their nests in the branches, and the great shadow that it gives.
It has become a symbol of peace after the Second World War: in fact, only a few of these trees bravely survived the devastating atomic blast in Nagasaki. Although it was one of the oldest fruit trees cultivated by man, it is said that the first persimmon tree was cultivated in Italy in the Boboli Gardens, only in 1871.
Immature fruits are collected and consumed in winter, after a complete ripening.
Diospyros kaki - Wikipedia
Cachi
Description
It is estimated that 100 grams of persimmon provide approximately 65-70 kcal (equivalent to about 272 kJ). Water constitutes about 80% of the fruit, sugars as much as 16-18%, while the fibers are calculated at around 2.5%, protein 0.6% fat 0.2%.
It is also rich in mineral salts, mainly potassium (161 mg%), phosphorus (17 mg%), magnesium (9 mg%), calcium (8 mg%) and sodium (1 mg%), while selenium and manganese are only present in traces.
It contains a large amount of vitamin A (1627 IU), mainly derived from beta-carotene, vitamin C (from 7 to 50 mg for 100g depending of ripening degree), vitamin K (2,6 mcg) and some natural pigments that give it its beautiful colour, as lycopene (159 mcg), carotenoids (253 mg), lutein and zeaxanthin (834 mcg).
Choline is rather rapresented (7.6 mg), while tannins are more present in unripe fruits.
Cachi: Valori nutrizionali e composizione
It is known, due to its nutritional composition, that persimmons have different properties regarding health.
- Prevention of cardiovascular diseases
Recently has been shown, that the high content of polyphenols and tannins in persimmon is significantly able to prevent atherosclerosis in mice to which it is administered with the diet.

Influence of two cultivars of persimmon on atherosclerosis indices in rats fed cholesterol-containing diets
Tannins also called proanthocyanidins, have strongly antioxidant properties and they can also act synergistically with ascorbic acid. They reduce platelet aggregation, and can help to decrease the risk of damage to the coronary arteries.
Modulation of Oxidative Stress by Proanthocyanidin in H2O2-Exposed Human Diploid Fibroblast Cells
In Japan, persimmon juice and vinegar are used in traditional medicine in order to low blood pressure.
Some Japanese authors have shown that the fruit and the extract of persimmon leaves are able to inhibit significantly the secretion of endotelin-1 and improve the production of nitric oxide in order to induce vasorelaxation.
Bioactive-rich extracts of persimmon, but not nettle, Sideritis, dill or kale, increase eNOS activation and NO bioavailability and decrease endothelin-1 secretion by human vascular endothelial cells.
Evaluation to the antioxidant activity of total flavonoids extract from persimmon leaves.
Although in the past persimmons were not recommended in low-calories diets for theirs considerable sugar amount, recently it is proved that eating them, can prevent rapid increases of blood sugar level after the intake of a meal high in carbohydrates. This apparently contradictory effect, promoted by persimmon peel and leaves extract, full of antioxidant agents, is due to the inhibition of enzime alpha-amylase. The inhibition of this enzime by polyphenols, slows down the digestion of starch in foods and improves peripheral glucose utilisation.

Inhibitory activities of proanthocyanidins from persimmon against oxidative stress and digestive enzymes related to diabetes.
A review on structure-activity relationship of dietary polyphenols inhibiting α-amylase.
Others substances contained in persimmons leaves, as vomifoliol 9-O-α-arabinofuranosy, are able to inhibit intestinal alpha-glucosidase activity, so it can be used as an insulin-sensitizing agent against type 2 diabetes.
Vomifoliol 9-O-α-arabinofuranosyl (1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside from the leaves of Diospyros Kaki stimulates the glucose uptake in HepG2 and 3T3-L1 cells.
Influence of different extracts from persimmon leaves on the antioxidant activity in diabetic mice.

Carotenoids, such as lycopene, and proanthocyanidins (epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate) are resulted effective, both in vitro and in vivo against a wide range of cancers, particularly breast cancer , lymphoid leukemia , lung adenocarcinoma and pre-cancerous colon polyps.
Effects and action mechanism of Diospyros kaki on the differentiation of human leukemia HL-60 cells.
Persimmon leaf extract inhibits the ATM activity during DNA damage response induced by Doxorubicin in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells.
The relationship between intake of vegetables and fruits and colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence.
Induction of programmed cell death (apoptosis) in human lymphoid leukemia cells by catechin compounds.
Induction of apoptosis in human cancer cell lines by diospyrin, a plant-derived bisnaphthoquinonoid, and its synthetic derivatives.
They also have a suppressive effect on the proliferation of human pancreatic cancer cells, through the inhibition of DNA-polymerase, by inducing apoptosis. Even 24-hydroxyursolic acid, which is contained in persimmons leaves, has a recognized antineoplastic effect: it inhibits cell proliferation by the strongly activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). It can also induce apoptosis by activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP).
24-hydroxyursolic acid from the leaves of the Diospyros kaki (Persimmon) induces apoptosis by activation of AMP-activated protein kinase.
Chemical constituents of the leaves of Diospyros kaki and their cytotoxic effects.

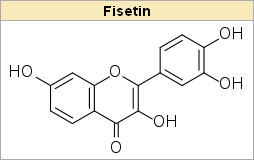
Persimmons have a large amount of flavonoids including fisetin, which is reported to have effective anti-inflammatory and anticarcinogenic properties.
Fisetin: a dietary antioxidant for health promotion.
Diospyrin, a substance conteind in this fruit, has a selective cytotoxicity against tumor cells, in fact it is not able to damage normal human lymphocytes in vitro.
Induction of apoptosis in human cancer cell lines by diospyrin, a plant-derived bisnaphthoquinonoid, and its synthetic derivatives.
The antibacterial effect is due to the action that tannins have on the bacterial cell wall. Tannic acid activity is able to inhibit biofilm formation by Gram-positive bacteria as Staphylococcus aureus, without inhibiting bacterial growth.
Then consume foods rich in polyphenols such as persimmon may be able to influence Stapylococcus aureus surface colonization.
Tannic acid inhibits Staphylococcus aureus surface colonization in an IsaA-dependent manner.
It is known that persimmon vinegar is able to reduce intoxication from alcohol. Experiments on alcohol-fed mice, have shown that the introduction of persimmon vinegar in the diet significantly decreased serum triglyceride and total cholesterol, and liver total cholesterol levels. This dose-dependent effect, is due to the stimulation of hepatic carnitine palmitoyltransferase-I promoted by carotenoids.
Effects of persimmon-vinegar on lipid metabolism and alcohol clearance in chronic alcohol-fed rats.
Carotenoids extraction from Japanese persimmon (Hachiya-kaki) peels by supercritical CO 2 with ethanol.

Conclusion
Persimmons also contain simple sugars, very easy to absorb, and then quickly provide energy.
It is rich in copper, trace element that enhances the immune system.
As is shown this fruit from the many virtues is also diuretic, laxative and cleansing for the liver.
For their high calorific value, are not recommended for obese people and in those who suffer from gastrointestinal disorders.
Recently it also has been proved in vitro, the anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects of the extract of persimmon, which is able to inhibit the release of histamine from mast cells by modulating cAMP and intracellular calcium levels. The aqueous extract decreased gene expression and the secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α and IL-1β by inhibiting nuclear factor-κB. Its effect is similar to an anti-allergy drug such as disodium cromoglycate.
Inhibitory effects of Diospyros kaki in a model of allergic inflammation: role of cAMP, calcium and nuclear factor-κB.