Kegg Pathway
DEFINITION
ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC-transporter) are members of a protein superfamily that is one of the largest and most ancient families.
They are transmembrane proteins that utilize the energy of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) hydrolysis to carry out certain biological processes including:
- translocation of various substrates across membranes (metabolic products, lipids and sterols, and drugs)
- non-transport-related processes such as translation of RNA and DNA repair
Proteins are classified as ABC transporters based on the sequence and organization of their ATP-binding cassette (ABC) domain(s).
ABC transporters are involved in tumour resistance, cystic fibrosis, bacterial multidrug resistance, and a range of other inherited human diseases.
MAMMALIAN ABC TRANSPORTERS IN HEALTH
AND DISEASE 2002
External links not available on Wikipedia have to be added here
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE AND IMAGES
When relevant for the function
- Primary structure
- Secondary structure
- Tertiary structure
- Quaternary structure
Protein Aminoacids Percentage
The Protein Aminoacids Percentage gives useful information on the local environment and the metabolic status of the cell (starvation, lack of essential AA, hypoxia)
Model (Width 600 px)

SYNTHESIS AND TURNOVER
mRNA synthesis
protein synthesis
post-translational modifications
degradation
CELLULAR FUNCTIONS
cellular localization,
biological function


- Enzymes
- Cell signaling and Ligand transport
- Structural proteins
REGULATION
DIAGNOSTIC USE
ABC_transporter W
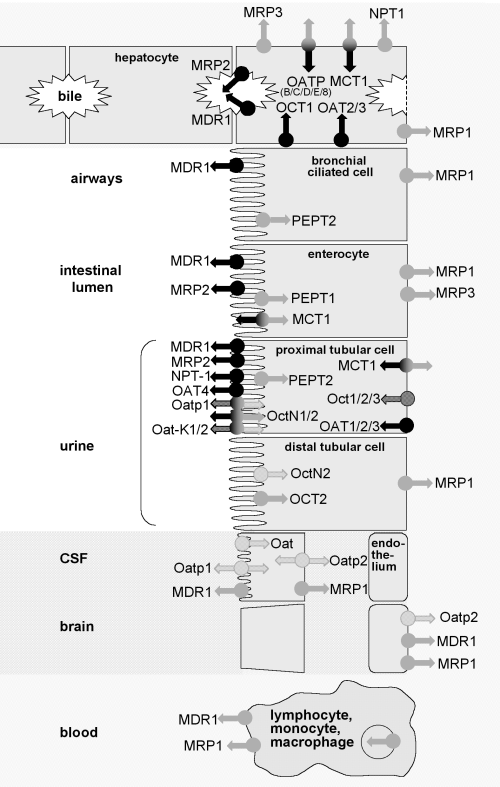
Transporter specificity
MDR1
49 Human ATP-Binding Cassette Transporters