Definition
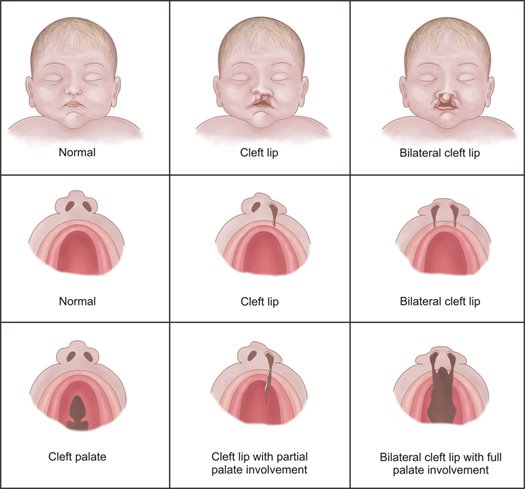
Orofacial clefts are congenital malformations characterized by incomplete formation of structures separating the nasal and oral cavities: lip, alveolus, hard and soft palate.
We can find three variations of this disease:
- Cleft lip (cheiloschisis, CL)
- Cleft palate (palatoschisis, CPO)
- Cleft lip and palate (cheilopalatoschisis, CLP)
Epidemiology
The average incidence of CLP is 1-2 per 1000 live births.
Epidemiological studies in Italy has demonstrated that cleft palate as well as right sided clefts are more frequent in females, while left sided clefts are more frequent in males.
Literature sources:
Carinci F, Rullo R, Farina A, Morano D, Festa VM, Mazzarella N, Del Viscovo D, Carls PF, Becchetti A, Gombos F. , Non-syndromic orofacial clefts in Southern Italy: pattern analysis according to gender, history of maternal smoking, folic acid intake and familial diabetes. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2005 Apr;33(2):91-4.
Symptoms
Orofacial clefts are usually identifiable at birth as an opening or split in the upper lip, the palate or both.
Other symptoms includes:
- Swallowing problems
- Feeding problems
- Flow of milk through nasal passages during feeding
- Recurrent ear infections
- Speech difficulties
- Misaligned teeth
- Change in nose shape
Diagnosis
Prenatal diagnosis includes:

After birth a physical examination of the mouth, nose, and palate confirms a cleft lip or cleft palate.
Embryological signs
Development of the face

Pathogenesis
Oral cleft is a defect of formation of the frontonasal proces by wich nose, superior lip, maxilla and primary palate take origin, or is a defect of the fusion of the frontonasal proces with the two maxillary processes. These two anomalies are caused by defects of neural tube.
The pathogenesis of cleft lip and cleft palate is complex; the most widely accepted model is the multifactorial inheritance (Carter, 1969;Fraser, 1970), according to wich this pathology is connected to the interaction of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic Factors:
- Syndromic cases:
- Non syndromic cases:
- OFC1 (locus 6p23-p24)
- OFC2 (locus 2p13)
- OFC3 (locus 19q13)
- OFC4 (locus 4q21-q31)
- OFC5 (gene MSX1)
- OFC6 (gene IRF6)
- OFC7 (gene PVRL1)
- OFC8 (gene TP73L)
- OFC9 (locus 13q33.1-q34)
- OFC10 (gene SUMO1)
- RARA (locus 17q21.1)
- TGFB3 (locus 14q24)
- MTHFR
Environmental Factors:
Prevention Factors
Literature sources:
- Maternal dietary B vitamin intake
- “Folate intake
- Folic acid on prevention of orofacial cleft
Complications

- Psychosocial issues
- Infections (otitis media, pneumonia, bronchopneumonia)
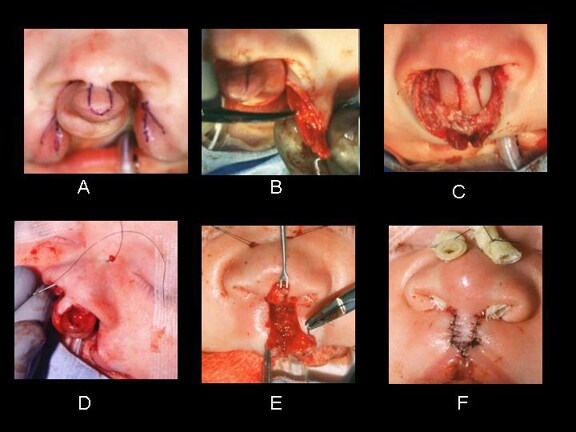
- Plastic surgery
- Oral and maxilofacial surgery
Alessio Parrotta – Giorgia Corrias