DEFINITION
Piroxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (FANS) forming part of Oxicam , characterized by a long duration of action and a long half-life, well indicated for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
These compounds are used in the symptomatic treatment of inflammation associated with rheumatic diseases such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
CLASSIFICATION
Belonging to the class of heterocyclic carboxyamide benzotiazinic, is the founder of the most well-known category of Oxicams. Most of the drugs in this class is a non-selective COX inhibitor, for the exception of the so called Meloxicam that has a slight preference, approximately 10:1, for the COX-2

INDICATIONS
The main indication of Piroxicam is the symptomatic treatment of inflammation associated with rheumatic diseases such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis.
Different studies have also shown how this active substance may even carry out an antioxidant and istoprotective function, protecting both tissues from oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide and both by inhibiting the activity of different proteases involved in tissue lesions.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Taken orally or rectally, is absorbed by the intestinal mucosa, reaching peak plasma concentrations maximum after about 8 hours, and persisting in the circulation for more than 24 hours, even 72 or 80. The piroxicam has the distinction of being slowly metabolized and eliminated by the kidneys as slowly; these properties involve plasma half-life to allow once-daily dosing. Bound to plasma protein is distributed in the circle, concentrating mainly at the level of synovium and joints, where massively carry out its therapeutic potential.
After its biological activity, the Piroxicam is metabolized in the liver and eliminated in the form of glucoronati inactive catabolites, mainly through the urine.
There is also the Piroxicam in the form of gel for topical therapy (Antiflog Gel).
MOLECULAR MECHANISM
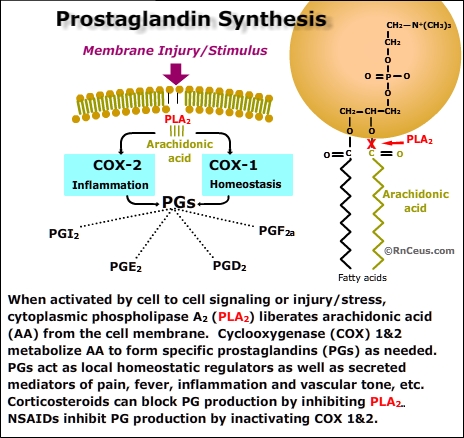
Piroxicam is a reversible non-selective cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor. Is able to reduce the production of chemical mediators known as prostaglandins, involved in the recruitment of inflammatory cells, in lowering the pain threshold and in the genesis of the stimulus pyrogenic.
At high doses, the piroxicam is also able to inhibit leukocyte migration and leucopoiesis.

PHARMACOGENOMICS
Cytochrome CYP2C9 , which is part of the big family of Cytochrome P-450, is the major pathway for the metabolism of piroxicam. Patients who are poor CYP2C9 metabolizer have their clearence of piroxicam reduced up to 30-fold. In most cases, the effects of allele 3 on drug clearence were more marked than for those of allele 2.
SIDE EFFECTS
About 30% of those who make use of piroxicam develop adverse effects which include:
- Dizziness
- Tinnitus
- Headache
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Rashes.
Furthermore, administration of more than 20 mg / day of piroxicam involves an increased incidence of peptic ulcer and bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract of 9.5 higher than the other NSAIDs. [6] In addition, the solar exposure during therapy with piroxicam should be avoided due to photosensitivity
Particular attention should be given to patients taking Piroxicam and simultaneously with liver disease, renal, gastrointestinal and cardiovascular diseases, given the greater susceptibility of these side effects of the drug.
Feldene has also high allergenicity and even if consequences are rare, in patients with allergic and dermatological diseases, can occur toxic epidermal necrolysis.
TOXICITY
Piroxicam is associated with an incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events and serious skin problems greater than the other FANS.
Gastric Toxicity: GI bleeding, ulceration and perforation can occur at any time during treatment with NSAIDs even in the absence of warning signs. The risk of gastric toxicity is greater in the case of treatment with high doses and in the presence of risk factors such as history of ulcer, particularly if complicated with haemorrhage and / or perforation, old age.
Dermal toxicity: treatment with NSAIDs has been associated in rare cases with very severe cutaneous toxic effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Asthmatic patients: as piroxicam interferes with the metabolism of arachidonic acid, in susceptible patients with asthma or bronchospasm may occur, shock, and other allergic events.
Renal impairment: piroxicam can cause acute renal failure, especially in cases of impaired renal function, elderly patients, diuretic treatment contemporary. The onset of acute renal failure may be due to a change in renal blood flow induced by inhibition of renal prostaglandins, prolonged treatment with NSAIDs may cause interstitial nephritis, glomeruliti, nephrotic syndrome.
Lactose: in the case of hereditary galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption, the medicinal product is contraindicated because it contains lactose excipients between.
Topical treatment: topical treatment prolonged contact may cause sensitization that may require supportive therapy or discontinuation of treatment. The topical treatment is typically associated with a lower risk of adverse effects because the serum concentrations are lower than those obtained with the administration of systemic medication.
INSTRUCTION FOR USE AND DOSAGE
 Feldene ®
Feldene ®
Capsules of 20 mg of piroxicam;
Soluble tablets of 20 mg of Piroxicam;
Suppositories 20 mg of Piroxicam.
Ampoules intramuscularly from 20 mg of piroxicam per ml of solution.
Treatment with piroxicam, in the light of its side effects, should be supervised by a physician experienced in the treatment of rheumatic diseases, which should define the effective dose based on the physio-pathological characteristics of the patient, the severity of the clinical picture and the therapeutic goals to reach.
Given the half-life of the active principle, the mono-daily administration of this drug should be able to provide coverage for all 24 hours.
In order to reduce the incidence of possible side effects, it would be desirable to limit the intake of Feldene ® for the shortest time possible and at the lowest effective dose.
OTHER STUDIES
- Piroxicam, as Meloxicam, seems to have even antioxidant functions ameliorating hepatic ossidative stress abd damage in the ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Piroxicam and meloxicam ameliorate hepatic oxidative stress and protein carbonylation in Kupffer and sinusoidal endothelial cells promoted by ischemia-reperfusion injury
- Always for his antioxidant activity, common to the other NSAID's, researchers are interested in his potential inhibition of acquaporin-4 and Acid Sensing Ion Channel 1a (ASIC1a) in cerebral ischemia.
Neuroprotective potential of Piroxicam in cerebral ischemia: an in silico evaluation of the hypothesis to explore its therapeutic efficacy by inhibition of aquaporin-4 and acid sensing ion channel1a
- In animal models with oral squamous cell carcinoma, very similar to the human one, it has been show that Piroxicam lows COX2 increased by the treatment with Mastinib which inhibit AKT signalling pathways.
Piroxicam inhibits Masitinib-induced cyclooxygenase 2 expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro