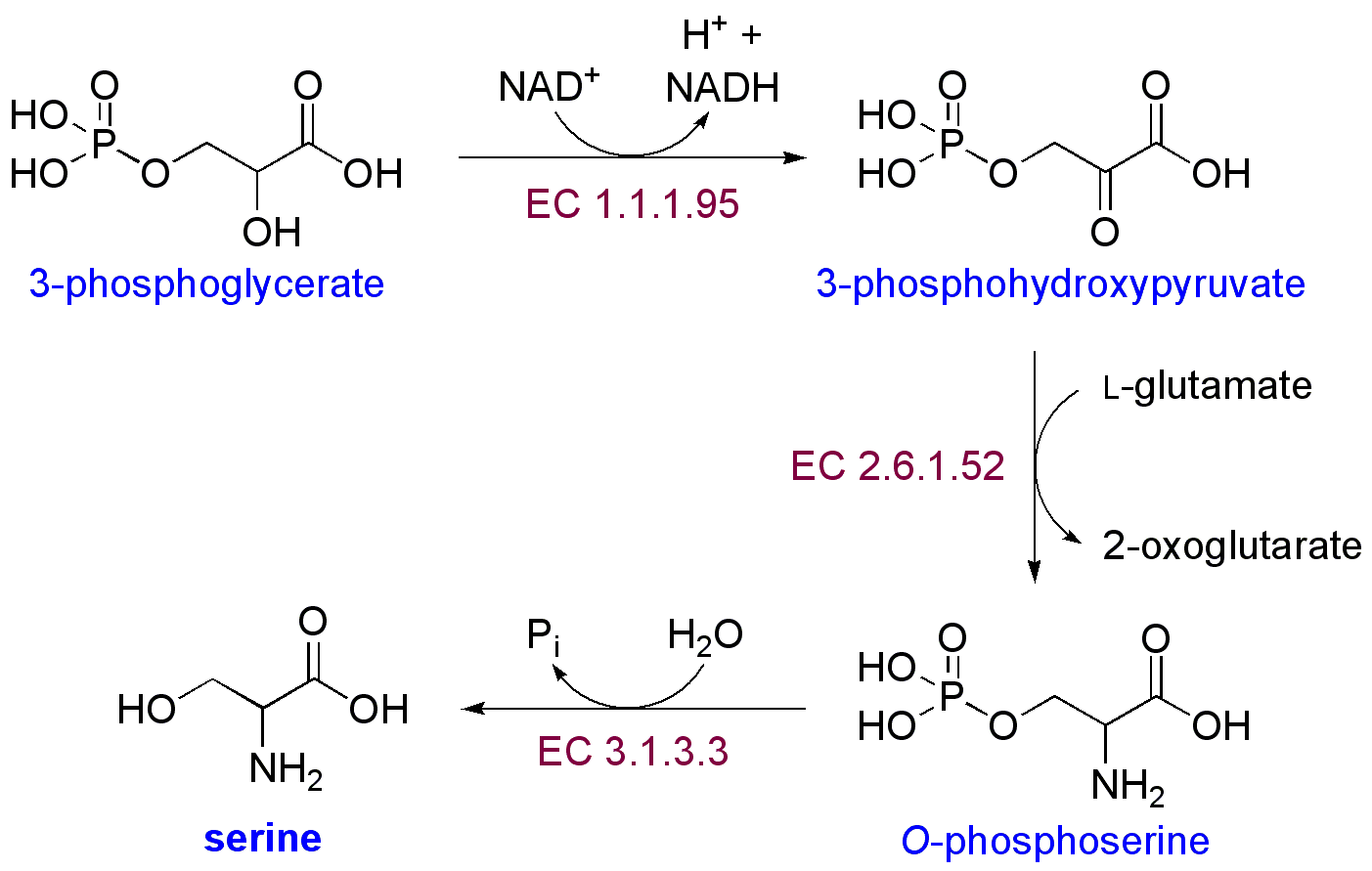
Synthesis
Degradation
To 2-P-glycerate

To Glycine
The main pathway to glycine is a 1-step reversible reaction catalyzed by serine hydroxymethyltransferase This enzyme is a member of the family of one-carbon transferases and is also known as glycine hydroxymethyltransferase. This reaction involves the transfer of the hydroxymethyl group from serine to the cofactor tetrahydrofolate (THF), producing glycine and N5,N10-methylene-THF.
Serine/glycine mitochondrial
Glycine produced from serine or from the diet can also be oxidized by glycine decarboxylase (also referred to as the glycine cleavage complex, GCC) to yield a second equivalent of N5,N10-methylene-tetrahydrofolate as well as ammonia and CO2.