Premesse
La mortalita' dipende dall'eta'

La mortalita' dipende dal sesso e da altre malattie preesistenti
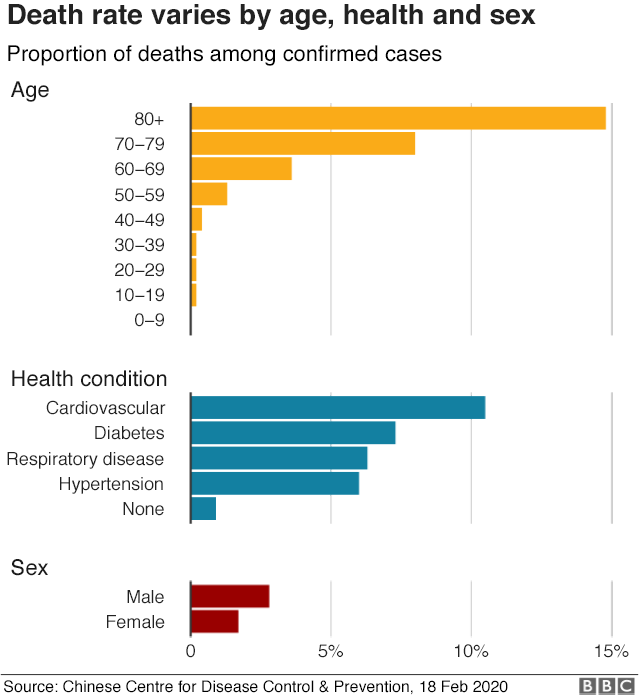
Quali sono le variabili che rendono diversi giovani e vecchi, maschi e femmine, sani o sofferenti di alcune patologie?
Come posso capire il mio grado di rischio?
| Fattore di rischio | DHEA | Cortisolo | GSH | Vit D |
| Età | basso | alto | basso | basso |
| Diabete | basso | alto | basso | basso |
| Ipertensione | basso | alto | basso | basso |
| Diuretici?? | - | alto | - | - |
| Farmaci | - | - | basso | basso |
| Inquinamento Atmosferico | - | - | basso | basso |
DHEA, cortisolo, GSH non sono misurabili con i normali esame di sangue. La tabella ha solo valore indicativo per fare capire come i diversi fattori di rischio si sommano, attraverso i meccanismi comuni
Che accorgimenti posso utilizzare per rendere tutti il piu' simile possibile a una donna giovane e sana?
Ormoni
E' chiaro che molti ormoni (DHEA, Testosterone, Estrogeni) scendono con l'eta', ma la terapia sostitutiva in questo caso deve essere personalizzata da un medico
Siccome è possibile modulare il livello del GSH con supplementi alimentari (NAC/N-acetyl cysteine 600 mg e glycine 500/1000 mg al mattino) la loro somministrazione può essere un giustificato approccio alla prevenzione e alla riduzione dei sintomi.
Le dosi suggerite sono quelle normalmente usate e sono liberamente reperibili sul mercato, anche in Internet.
Sono molto inferiori a quelle usate nel lavoro citato per far ritornare il valore del GSH degli anziani al valore dei giovani. Tali dosi più elevate pero' devono essere prese sotto controllo medico e non su iniziativa personale.
Ferro
Anche la carenza di ferro aumenta la gravità della risposta infiammatoria (iron deficiency and inflammation). La carenza di ferro va curata, ma anche in questo caso la terapia va personalizzata dal medico.
Colesterolo
Disturbi della sintesi del colesterolo su base genetica (colesterolo troppo alto o troppo basso), secondari ad altre malattie (ipotiroidismo) o all'uso di farmaci possono portare ad un aumento della risposta infiammatoria.
Un adeguato controllo medico di queste situazioni riduce il rischio di infiammazione.
Avviso importante:
Attualmente non ci sono strumenti terapeutici per impedire la diffusione del virus, ma possiamo cercare di diminuire l'infiammazione prodotta dall'infezione. Tanto più sono infiammati i polmoni tanto meno riesco a scambiare ossigeno. A parte il sentirsi mancare l'aria (soggettivo) si può misurare la saturazione di ossigeno e la frequenza cardiaca, che aumenta al calare dell'ossigeno (dati oggettivi).
La misura può essere fatta facilmente da chiunque con un pulsossimetro da dito (Cercalo).
Non ho idea di quali siano le attuali indicazioni nel corso di questa epidemia, ma finora in Ospedale si preoccupavano del tuo ossigeno sotto il 90%.
L'ossigeno puo' diminuire nel tuo corpo perche' diminuisce la sua pressione parziale nell'aria, per via del calo della pressione atmosferica o dell'aumento di umidità.
Prima di allarmarti per un calo della tua saturazione controlla le variazioni ambientali:
Pressione Atmosferica Umidita' relativa
Lavori pubblicati
The Role of Glutathione in Protecting against the Severe Inflammatory Response Triggered by COVID-19, 2020
Tutti i lavori su COVID-19 e GSH
In coperazione con Barend Mons
Mild as well as severe disease caused by COVID-19 might be part of the same problem: Machine-assisted analysis of congruent clinical observations and the underlying molecular mechanisms in order to rationalise drug repurposing 2020
Altri autori
Accademia delle Scienze di Torino: Covid-19
Rapporto Covid Epidemia di Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei - Commissione Salute
Evoluzioni del discorso
Proposta per la Fase 2: come ridurre i sintomi dell’infezione da SARS-CoV-2 e identificare gli individui a rischio di malattia, 14 04 20 fatto pervenire al CTS
Il modo più semplice per accedere alle informazioni sull'argomento è cercare con Google: Pescarmona NAC
Terna P., Pescarmona G., Acquadro A., Russo G., Pescarmona P., Terna S. (2020), An Agent-Based Model of the Diffusione of Covid-19 Using NetLogo, 08 05 20220
Video Seminario Centro Einaudi Venerdi 8 Maggio 2020. Presentazione del Modello: Prof. Pietro Terna, (dal min 3/20 ca). Le Basi Biochimiche (io, dal min 20/40 ca). Segue Discussione di circa 1 ora
Testo Presentazione Pescarmona
Ottobre 2020
20 ottobre 2020 - Mondo Economico - Opinioni
Emergenza Covid: una lettura medica e sociale sui piu deboli. Pescarmona Terna
Emergenza Covid come gestire il contagio dei dati. Russo Terna
HOW CAN ABM MODELS BECOME PART OF THE POLICY-MAKING PROCESS IN TIMES OF EMERGENCIES – THE S.I.S.A.R. EPIDEMIC MODEL
Citazione su La Stampa 22 10 2020
23/10/2020

l'impennata dei picchi parte alla fine di settembre. Perchè?
Le scuole sono iniziate da tempo e l'età media è alta...
E se non dipendesse da noi?

Weatheronline
il freddo favorisce la comparsa delle infezioni stagionali delle vie aeree
Maria Rita Gismondo sul senso dei numeri
25/10/2020
sulla base delle argomentazioni descritte nei precedenti link la strategia preventiva piu' sensata appare:
- Aumentare il livello del GSH con supplementi alimentari liberamente acquistabili (NAC/N-acetyl cysteine 600 mg e glycine 500/1000 mg al mattino). Tale integrazione può essere assunta per mesi/anni senza effetti collaterali.
- Aumentare il livello di Vitamina D con l'uso del calcidiolo (Didrogyl 1goccia ogni 10 kg di peso) acquistabile con ricetta medica e controllandone l'effetto
- Aumentare il metabolismo basale, soprattutto nei piu' anziani. Per ottenere questo occorre una corretta valutazione dello stato nutrizionale e ormonale (tiroide e surrene) che deve essere corretto con una terapia sostitutiva adeguata, da valutarsi da parte del medico (selenio, iodio, vitamine, ormone tiroideo, DHEA)
26/10/2020
identificazione dei soggetti fragili
09/11/20
Statistiche e dati sul COVID-19
16/01/21
COVID-19: l’economia e la malinconia della scienza su Mondo Economico
COVID-19: l’economia e la malinconia della scienza. Mio PDF
19/08/21
Lavoro in pubblicazione su Crowd Dynamics, Volume 3, Ed. N. Bellomo, Springer
Preprint su arXiv
An Agent-Based Model of COVID-19 Diffusion to Plan and Evaluate Intervention Policies
La parte sulle basi molecolari dell'infezione è da pagina 4 a 7.
Fattori di rischio ambientali
Il distanziamento sociale, le goccioline nell'aria, le strade.
ma c'è qualcosa di cui non avevamo ancora sentito parlare: l'uso dei contanti che in Spagna e in Italia è molto diffuso.
Pensateci e usate il vostro Bancomat
Contatto
Per eventuali commenti, domande, eccetera. scrivere a:
paziente.responsabile@gmail.com