Description
Phenylalanine is an essential, non polar, large α-amino acid.


The codons for L-phenylalanine are UUU and UUC.
Source
Phenylalanine is contained in most protein rich foods, but especially good sources are dairy products (curd, milk, cottage cheese), avocados, pulses and legumes (particularly peanuts and lima beans), nuts (pistachios, almonds), seeds (piyal seeds), leafy vegetables, whole grains, poultry, fish and other seafoods).

Metabolism
L-phenylalanine can be converted into L-tyrosine by Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH)

Phenylalanine uses the same active transport channel as tryptophan to cross the blood-brain barrier, and, in large quantities, interferes with the production of serotonin.
Tyrosine is an aromatic amino acid that is found in large quantities in casein
L-tyrosine is converted into L-DOPA, which is further converted into dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline) (the latter three are known as the catecholamines).
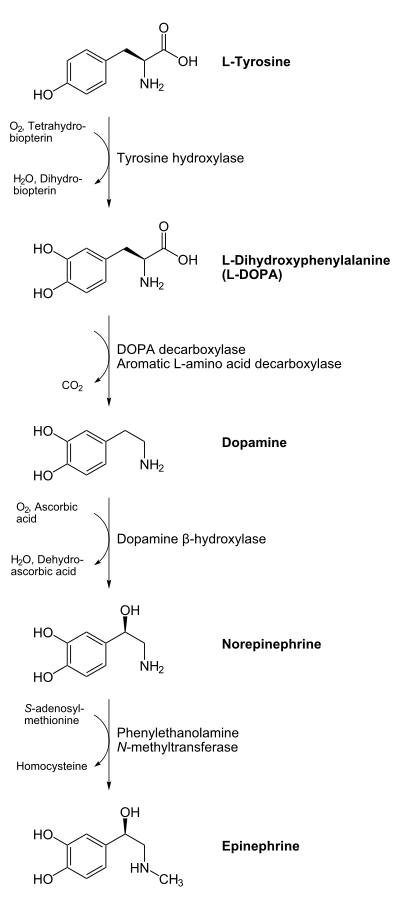
In the first two reactions, L-Tyrosine is converted into L-DOPA by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase, using tetrahydrobiopterin (THB), O2, and ferrous iron (Fe2+) as cofactors.
L -DOPA is converted into dopamine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase, using pyridoxal phosphate (PLP).
The native dopamine is stored in vesicles and when an action potential occurs, it is secreted by presynaptic cell Once in the synapse, dopamine binds to and activates postsynaptic dopamine receptors (D1 - D5) and after it has performed its synaptic duties , it is taken up via reuptake back into the presynaptic cell and re-stored into vesicles.
Below there is dopamine degradation:

The two important enzymes are monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). Homovanillic acid (HVA) is the final product of the metabolic pathway excreted in the urine.

Tyrosine Kegg Pathways
a deeper insight

Estimation of Km values of enzymes requiring molecular O2 as a substrate, 1981
Melanin Synthesis

A review of recent advances on the regulation of pigmentation in the human epidermis.
!Papers RhoA, Rac and Melanin
Y/P relationships

Dopamine
Tyrosine catabolism

more details....!
Fumarylacetoacetase (FAH) deficiency leads to Tyrosinemia, type 1

Succinylacetone accumulation leads to heme synthesis inhibition.