Eyes are organs that detect light
Open Question: how eyes developed during fetal life in the absence of light?

The human eye contains two types of receptors that respond to light: cones and rods.

Open Question: why the sensors cells how eyes developed during fetal life in the absence of light?

Retinal pigments
Different Organisms See Different Worlds
Fish Vision
Human eye
Eye color vision
Human cones come in three varietys, indentified as S, M, and L, that are sensitive to short, medium, and long wavelengths of light, respectively.

S 445 nm blue light
M 540 nm green
L 565 nm red

The L cones are most abundant (63%), followed by M cones (31%) and a small number of S cones (6%).

Bipolar cell pathways in the vertebrate retina, 2007
Int J Neurosci. 1998 Jul;95(1-2):115-32.
Excitatory amino acids and serotonin uptake blockers reveal two physiologically distinct serotonin systems in the retina of the skate, Raja erinacea.
Schuette E, Chappell RL.
Hunter College and the Graduate School of the City University of New York, Department of Biological Sciences, NY 10021, USA.
The retina of the skate (Raja erinacea) contains at least 2 types of cell (amacrines and bipolars) that can be visualized with an antiserum against serotonin. We have employed serotonin immunocytochemistry in combination with pharmacological manipulation of retinal tissue to analyze physiological properties of serotonergic amacrine cells and serotonin-accumulating bipolar cells. Excitatory amino acids (NMDA, aspartate) had no detectable effects on serotonin-immunoreactivity in bipolar cells but decreased staining in amacrine cells. High K+ Ringer increased staining in bipolar cell somata, however, it depleted the inner plexiform layer of the retina of serotonin. Zimelidine, a serotonin uptake inhibitor, completely blocked serotonin accumulation by bipolar cells but had no effect on amacrine cells, whereas incubation of the retinas in fluoxetine (Prozac), a different inhibitor of serotonin uptake, did not block serotonin accumulation into bipolar cells which was actually enhanced in some cases. We conclude that amacrine and bipolar cells of the skate retina employ two different serotonin uptake carrier systems, thus generating two distinct pharmacological components that are capable of interacting with each other as they compete for extracellular serotonin. Similar mechanisms may exist in the vertebrate CNS and further examination of the interaction of these systems could provide important insights into the action and possible side effects of serotonin-related drugs.
Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1998 Oct 30;61(1-2):243-50.
Circadian expression of tryptophan hydroxylase mRNA in the chicken retina.
Chong NW, Cassone VM, Bernard M, Klein DC, Iuvone PM.
National Institutes of Health Section on Neuroendocrinology, Laboratory of Developmental Neurobiology, 49/5A38, National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
Many aspects of retinal physiology are controlled by a circadian clock located within the eye. This clock controls the rhythmic synthesis of melatonin, which results in elevated levels during the night and low levels during the day. The rate-limiting enzyme in melatonin biosynthesis in retina appears to be tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH)[G.M. Cahill and J.C. Besharse, Circadian regulation of melatonin in the retina of Xenopus laevis: Limitation by serotonin availability, J. Neurochem. 54 (1990) 716-719]. In this report, we found that TPH mRNA is strongly expressed in the photoreceptor layer and the vitread portion of the inner nuclear layer; the message is also expressed, but to a lesser extent, in the ganglion cell layer. The abundance of retinal TPH mRNA exhibits a circadian rhythm which persists in constant light or constant darkness. The phase of the rhythm can be reversed by reversing the light:dark cycle. In parallel experiments we found a similar pattern of expression in the chicken pineal gland. However, whereas a pulse of light at midnight suppressed retinal TPH mRNA by 25%, it did not alter pineal TPH mRNA, suggesting that there are tissue-specific differences in photic regulation of TPH mRNA. In retinas treated with kainic acid to destroy serotonin-containing amacrine and bipolar cells, a high amplitude rhythm of TPH mRNA was observed indicating that melatonin-synthesizing photoreceptors are the primary source of the rhythmic message. These observations provide the first evidence that chick retinal TPH mRNA is under control of a circadian clock. Copyright 1998 Elsevier Science B.V.
bipolar cells retina serotonin
Eye neurons
MIT eye research

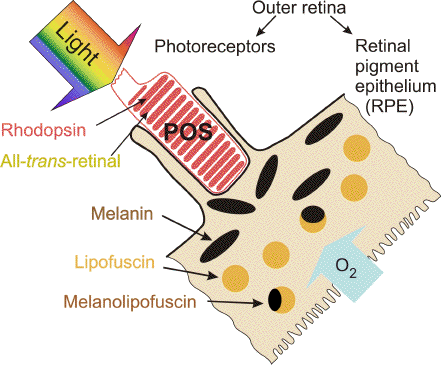
Pigmented layer
Differential response of red and green cones
S-Potentials and Horizontal Cells

Reference Textbooks
Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System - book thumbnail
Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System 2007
Eye Diseases

from Injectable_hydrogels_for_ophthalmic_applications, 2017