DEFINITION
Hypoxia inducible factors are transcription factors, that respond to changes in available oxygen in the cellular environment, increasing their activity in hypoxia.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE AND IMAGES
The highly-conserved transcriptional complex HIF-1, is a heterodimer composed of an alpha and a beta subunit. Both subunits belongs to the basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) proteins of the PAS FAMILY.
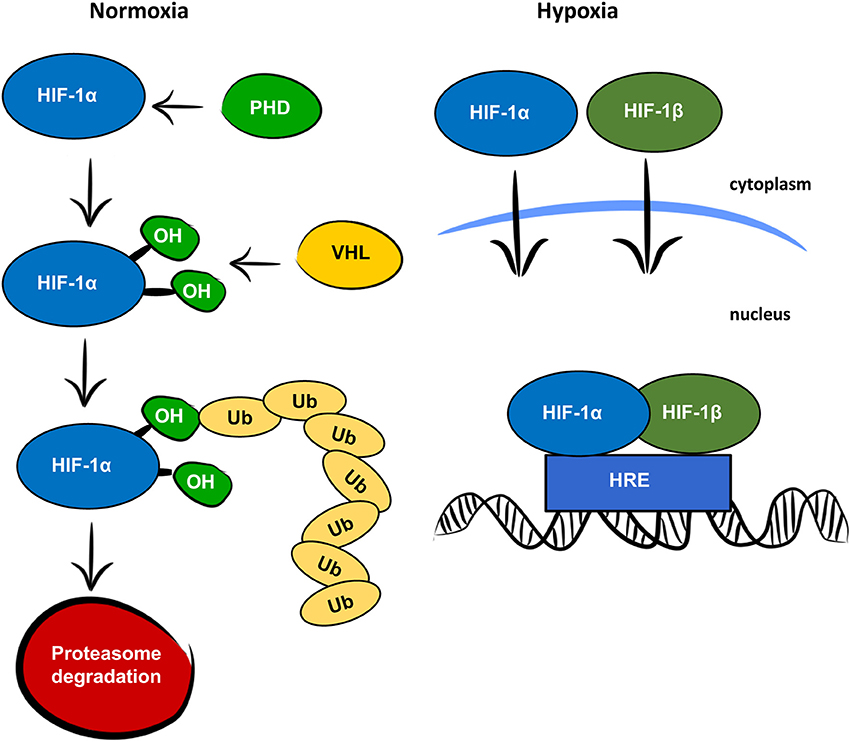
The HIFα/β dimer binds to a core DNA motif (G/ACGTG) in hypoxia-response elements ( HREs ).
Subunits
HIFα exists in 3 isoforms:
- HIF1α (5 isoforms reported)
- HIF2α
- HIF3α
HIFβ: a constitutively-expressed aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) that has been previously identified as a cytosolic dioxin receptor. It forms heterodimers also with AHR (OMIM 600253)and MOP2 (OMIM 603349)
When relevant for the function
- Primary structure
- Secondary structure
- Tertiary structure
- Quaternary structure
HIF (hypoxia) and VHL (normoxia) play antagonistic roles

SYNTHESIS AND TURNOVER
mRNA synthesis
protein synthesis
post-translational modifications and degradation
Under normoxic conditions HIF-1 alfa subunit has an exceptionally short half-life, it is subject to rapid turnover and degradation by the ubiquitin proteasome pathway.

Proteolytic regulation of HIF-1α is critically dependent on the von Hippel-Lindau tumour suppressor protein ( VHL). The ODD domain of HIFα subunits could physically interact with VHL and the VHL complex functioned as an ubiquitin ligase capable of ubiquitylating the HIFα subunits at normoxia and targeting them for destruction by the proteasome.
The ODD domain (oxygen-dependent degradation domain) contains N- and C- terminal portions ( N-ODD and C-ODD) that can operate independently.
The enzymatic reactions carried out by the PHD/HPHs and FIH-1 revealed that the hydroxylation reaction requires
- O2. The hydroxylation of proline and asparagine requires molecular oxygen
- Iron (Fe2+). PHD/HPHs and FIH-1 are Fe-dependent enzyme. Along with hypoxia, iron chelating agents such as desferoxamine were also able to block the enzymatic reactions and VHL interaction leading to stabilization of HIF-1alpha.
- 2-oxoglutarate (a citric-acid-cycle intermediate) is required because it undergoes a decarboxylation reaction, consuming the remaining oxygen atom to form succinate and CO2.
ROS (HCV, HBV, drugs )
Hypoxia
Local Iron Deficiency
- Global Iron Deficiency
- Lactoferrin, ferritin, Asbestos etc
- Herpesvirus infection (Ribonucleotide Reductase)
Molecular Mechanism of hypoxia and/or iron deficiency
Vitamin C and prolyl hydroxylase
ODD = oxygen - dependent degradation
VHL = von HIPPEL - LINDAU protein, E3 ligase
TAD = trans activation domain
CBP = coactivator binding protein
K = lys
P = pro
N = asn

Hypoxia blocked degradation leading to the accumulation of the HIF-1α protein in the citoplasm and its migration to the nucleus where binds HIFβ and form the HIFα/β dimer.
Oxygen level regulates the degradation via hydroxylation or acetylation-mediated VHL binding and also transcriptional activity of HIF-1:
- pVHL interaction is regulated by enzymatic hydroxylation at specific prolyl residues (for human HIF-1 , at Pro 402 in the NODD and at Pro 564 in the CODD). Therefore two proline hydroxylation sites had shown to promote VHL binding in a hydroxylation dependent manner.
- FIH (factor inhibiting HIF) hydroxylates N803 under normoxia and inhibits the association of p300/CBP to HIF-1 leading to the downregulation of transcriptional activity of HIF-1.
HIF oxygen-dependent hydroxylation


MDR:Multidrug resistance is the ability of pathologic cells to withstand chemicals that are designed to aid in the eradication of such cells. These pathologic cells include bacterial and neoplastic (tumor) cells
Hypoxia increases cell proliferation rate through reduction of glucose oxidative breakdown and induction of many enzymes (Glutamine synthetase, Glycolytic enzymes, G6PD etc). The high fetal growth rate is at least partially dependent on low fetal pO 2 .
Figure 1 Abreviations. VHL denotes von Hippel-Lindau protein, HIF hypoxia-inducible factor, TGF-{alpha} transforming growth factor {alpha}, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor A, PDGFbeta platelet-derived growth factor beta, EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, VEGFR2 VEGF receptor 2, PDGFRbeta PDGF receptor beta, PTEN phosphatase and tensin homologue, TSC1 and TSC2 tuberous sclerosis complex 1 and 2, FKBP12 FK506-binding protein 12 kD, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 kinase, eIF4E eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E, and S6K S6 kinase.
Used with permission from Brugarolas J. N Engl J Med 2007;356:185-187
HIF-1 alpha and ribosomal entry IRES
HIF Phosphorylation

CELLULAR FUNCTIONS
Generating specificity and diversity in the transcriptional response to hypoxia 2009
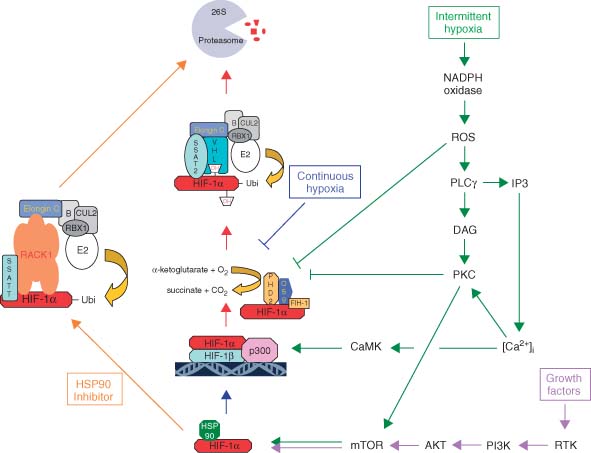
Oxygen homeostasis G. Semenza 2009
Genes induced by HIF

that are associated with a broad range of transcriptional targets. These target genes are centrally involved in:
- systemic responses to hypoxia ( angiogenesis, erythropoiesis)
- cellular responses (Cell proliferation, alterations in glucose and iron metabolism)
additional genes......
HIF-1 acts as a master regulator of oxygen-regulated gene expression. More than 60 putative HIF-1 target genes have been identified

HIF downstream effects
a deeper insight
cellular localization,
biological function
- Enzymes
- Cell signaling and Ligand transport
- Structural proteins
REGULATION
Cyclic AMP represses the hypoxic induction of hypoxia-inducible factors in PC12 cells.
Torii S, Okamura N, Suzuki Y, Ishizawa T, Yasumoto K, Sogawa K.
J Biochem. 2009 Dec;146(6):839-44. Epub 2009 Aug 11.
DIAGNOSTIC USE
HIF and symptoms
Symptoms dependent on VEGF (hyperexpression)
Increased vascular permeability:
- Edema
- Proteins efflux from vessels (urine, tissues)
- Effusions (pleural, pericardial, peritoneal)
Angiogenesis