Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin : Exists either covalently attached to another protein, or free (unanchored).
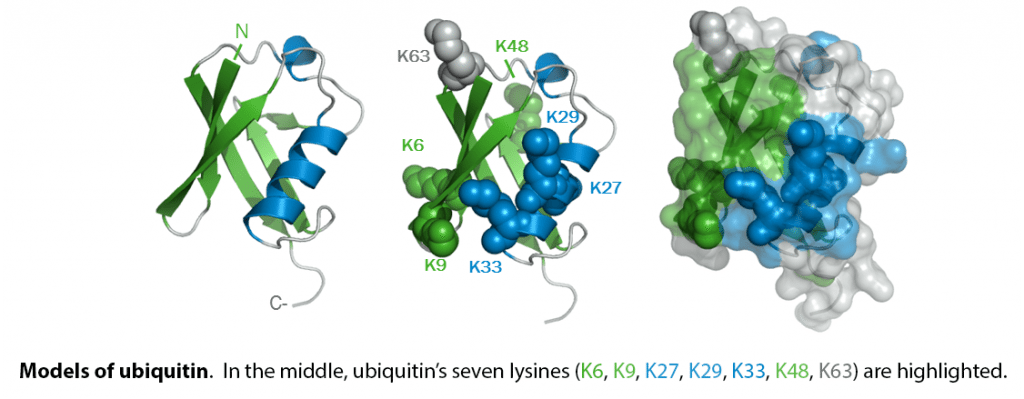
When covalently bound, it is conjugated to target proteins via an isopeptide bond either as a monomer (monoubiquitin), a polymer linked via different Lys residues of the ubiquitin (polyubiquitin chains) or a linear polymer linked via the initiator Met of the ubiquitin (linear polyubiquitin chains). Polyubiquitin chains, when attached to a target protein, have different functions depending on the Lys residue of the ubiquitin that is linked: Lys-6-linked may be involved in DNA repair; Lys-11-linked is involved in ERAD (endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation) and in cell-cycle regulation; Lys-29-linked is involved in lysosomal degradation; Lys-33-linked is involved in kinase modification; Lys-48-linked is involved in protein degradation via the proteasome; Lys-63-linked is involved in endocytosis, DNA-damage responses as well as in signaling processes leading to activation of the transcription factor NF-kappa-B. Linear polymer chains formed via attachment by the initiator Met lead to cell signaling. Ubiquitin is usually conjugated to Lys residues of target proteins, however, in rare cases, conjugation to Cys or Ser residues has been observed. When polyubiquitin is free (unanchored-polyubiquitin), it also has distinct roles, such as in activation of protein kinases, and in signaling.

from




Ubiquitin is encoded by 4 different genes. UBA52 and RPS27A genes code for a single copy of ubiquitin fused to the ribosomal proteins L40 and S27a, respectively. UBB and UBC genes code for a polyubiquitin precursor with exact head to tail repeats, the number of repeats differ between species and strains.
List of target proteins
BRCA1 Control of Steroid Receptor Ubiquitination 2007

A protein that interacts with the N-terminal region of BRCA1 (BRCA1-associated RING domain-1)

Viral activation of ubiquitination
Cellular protein degradation pathways can be utilized by viruses to establish an environment that favors their propagation. Here we report that the Kaposi's sarcoma–associated herpesvirus (KSHV)-encoded latency-associated nuclear antigen (LANA) directly functions as a component of the EC5S ubiquitin complex targeting the tumor suppressors von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) and p53 for degradation. We have characterized a suppressor of cytokine signaling box-like motif within LANA composed of an Elongin B and C box and a Cullin box, which is spatially located at its amino and carboxyl termini. This motif is necessary for LANA interaction with the Cul5–Elongin BC complex, to promote polyubiquitylation of cellular substrates VHL and p53 in vitro via its amino- and carboxyl-terminal binding domain, respectively. In transfected cells as well as KSHV-infected B lymphoma cells, LANA expression stimulates degradation of VHL and p53. Additionally, specific RNA interference–mediated LANA knockdown stabilized VHL and p53 in primary effusion lymphoma cells. Thus, manipulation of tumor suppressors by LANA potentially provides a favorable environment for progression of KSHV-infected tumor cells.

LANA is predicted to form a complex with Cul5/Rbx1 that interacts with Elongin BC but not LANA ΔSOCS (Cul box and BC box) mutant. LANA acts as adapter to link substrates which bind at its amino (1) or carboxyl (2) -terminal domain ( like VHL and p53 ) to EC5S ubiquitin complex and induces the pathway of ubiquitin E1 activation, E2 conjugation, and substrate polyubiquitylation as well as 26S proteasome–mediated degradation.
EC5S Ubiquitin Complex Is Recruited by KSHV Latent Antigen LANA for Degradation of the VHL and p53 Tumor Suppressors 2006 Fulltext