Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble prohormones, the two major forms of which are vitamin D2 (or ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (or cholecalciferol)
Vitamin D sources:
- food (D2)
Ref
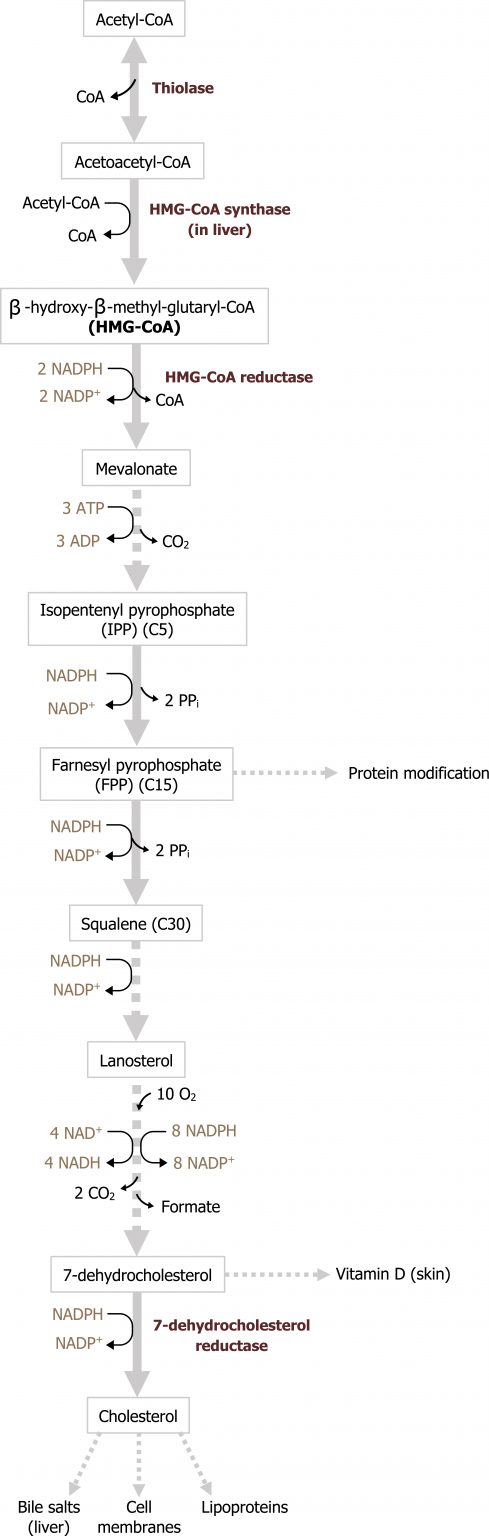
- skin after exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun (D3).

***

Vitamin D hydroxylation
Vitamin D requires chemical conversion in the liver, kidney and other tissues to form 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D, the physiologically active form of vitamin D.
.

The key kidney enzymes, the 25(OH)D3-1-hydroxylase and the 25(OH)D3-24-hydroxylase, as well as the liver vitamin D3-25-hydroxylase, are all known to be cytochrome P-450 mixed-function oxidases. Both of the renal enzymes are localized in mitochondria of the proximal tubules of the kidney. Mixed-function oxidases use molecular oxygen as the oxygen source instead of water. Mitochondrial mixed-function oxidases are composed of three proteins that are integral components of the mitochondrial membrane; they are renal ferredoxin reductase, renal ferredoxin, and cytochrome P-450.
Hydroxylation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 by renal mitochondria from rats of different ages. 1987
The age-dependent decrease in 1 alpha-hydroxylase and concomitant increase in 24-hydroxylase activities observed in mitochondria isolated from kidneys of 2-, 6-, 12-, 18-, and 24-month-old rats could not be attributed to changes in the bioenergetic properties, i.e. the respiratory chain (????), of the mitochondria.
Rat renal 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1- and 24-hydroxylases: their in vivo regulation. 1984
When vitamin D-sufficient rats having suppressed renal 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1-hydroxylase activity are placed on a low-calcium vitamin D-deficient diet for 7 days, the 1-hydroxylase activity is greatly stimulated in 6-wk-old rats but much less so in rats with advancing age.
A role for calmodulin in renal production of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. 1986
The calmodulin antagonists trifluoperazine (TFP), Janssen R24571, and the naphthalene sulfonamides W5 and W7 inhibited conversion of 25OHD3 to 1,25-(OH)2D3 by isolated renal tubules from vitamin D-deficient chicks in a dose-dependent manner (ED50: TFP, 12 mumol/liter; R24571, 10 mumol/liter; W7, 30 mumol/liter;
The renal mitochondrial metabolism of 25-hydroxyvitamin D-3: a possible role for phospholipids. 1986
Phosphatidylethanolamine and cardiolipin both brought about a dose-dependent decrease in the 1-hydroxylase activity in mitochondria from vitamin D-deficient chicks but not from vitamin D-replete chicks.
Vitamin D transport
Vitamin D is water insoluble and therefore requires specific proteins for plasma transport and cellular function
The role of plasma-binding proteins in the cellular uptake of lipophilic vitamins and steroids. 2006
Vitamin D cellular uptake
Vitamin D uptake into the cell depends on cubilin and megalin mediated endocytosis.
 .
.
Proximal tubule endocytic apparatus as the specific renal uptake mechanism for vitamin D-binding protein/25-(OH)D3 complex.
Chloroquine has been demonstrated to effectively reduce the extrarenal synthesis of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (Hypercalcemia associated with Wegener's granulomatosis and hyperparathyroidism: etiology and management. 1993)
Vitamin D trafficking to mitochondria
details

Vitamin D transport
Acute fluid shifts influence the assessment of serum vitamin D status in critically ill patients, 2010
Albumin binds to Vitamin D and, therefore, reductions in albumin will be accompanied by parallel reductions in the latter.
carrier for:
- Vitamin D
- 25(OH) Vitamin D
- 1,25(OH)2 Vitamin D
Vitamin D inactivation
The The key enzyme is, the 24(OH)-hydroxylase, active on both the 25(OH)D3 and the 1,25(OH2)D3 is mitochondrial
Vitamin D functions

Vitamin D exerts a complex pattern of actions
Genomic effects
Genes under VDRE control
The vitamin D hormone and its nuclear receptor: molecular actions and disease states. 1997
Vitamin D responsive elements (VDREs) consisting of direct hexanucleotide repeats with a spacer of three nucleotides have been identified in the promoter regions of positively controlled genes expressed in bone, such as osteocalcin, osteopontin, beta 3-integrin and vitamin D 24-OHase.
Large-scale in silico and microarray-based identification of direct 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 target genes. 2005
These experiments also revealed 16 VDREs in 11 of 12 genes induced more than 10-fold in our previous microarray study, five elements in the human gene encoding the epithelial calcium channel TRPV6, as well as novel 1,25(OH2)D3 target genes implicated in regulation of cell cycle progression.Ca 3000 genes (mouse)
Controlling the chromatin organization of vitamin D target genes by multiple vitamin D receptor binding sites. 2007
Taken together, both screening approaches suggest that a reasonable proportion of all VDR target genes, if not all, are under the control of multiple VDREs.
Plausible ergogenic effects of vitamin D on athletic performance and recovery. 2015
The hormonally-active form of vitamin D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, has been shown to play critical roles in the human body and regulates over 900 gene variants.
Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications. 2015
There are thousands of these binding sites regulating hundreds of genes in a cell-specific fashion.

The 1,25(OH)2D3 ligand promotes VDR-RXR heterodimerization and specific, high affinity VDRE binding on their promoter, whereas the ligand for RXR, 9-cis retinoic acid (9-cis RA), is capable of suppressing 1,25(OH)2D3-stimulated transcription by diverting RXR to form homodimers.
Major Target genes are: osteocalcin, osteopontin, beta 3-integrin, renin and vitamin D 24-OHase.
Vitamin D and calcium absorption

Renin
Renin expression is inhibited by 1,25(OH)2D3
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses renin gene transcription by blocking the activity of the cyclic AMP response element in the renin gene promoter. 2007

The vitamin D hormone and its nuclear receptor: molecular actions and disease states.
a deeper insight
1alpha,25(OH)2D3 induces capacitative calcium entry involving a TRPC3 protein in skeletal muscle and osteoblastic cells

Vitamin D and RANKL
Vitamin D and chemotaxis
Upregulation of vitamin D binding protein (Gc-globulin) binding sites during neutrophil activation from a latent reservoir in azurophil granules.

Genomic effects
Cyclin D3 interacts with vitamin D receptor and regulates its transcription activity.
Cyclin D3 promotes adipogenesis through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma.
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfotransferase is a target for transcriptional induction by the vitamin D receptor, 2004
Non Genomic effects
Vitamin D receptor is not required for the rapid actions of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 to increase intracellular calcium and activate protein kinase C in mouse osteoblasts.
Hydroxylase enzymes of the vitamin D pathway: expression, function, and regulation.
Activation of Src kinase in skeletal muscle cells by 1, 1,25-(OH)-vitamin D(3) correlates with tyrosine phosphorylation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) and VDR-Src interaction.
Open question: VDR nuclear translocation requires dephosphorylation that can be inhibited by cyclosporine ?
Clinical side effects of CsA
Calcium metabolism in adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus without and with persistent microalbuminuria.
Alterations in serum levels of 1 alpha,25(OH)2 D3 and osteocalcin in patients with early diabetic nephropathy.
Effect on NF-kappaB activity

Involvement of the vitamin D receptor in the regulation of NF-kappaB activity in fibroblasts.
Vitamin D regulates the phenotype of human breast cancer cells.
Increased NF-kappaB activity in fibroblasts lacking the vitamin D receptor.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism promotes the acute phase response -- a rationale for supplemental vitamin D in prevention of vascular events in the elderly.
Vitamin D physiology.
Vitamin D status affects serum parathyroid hormone concentrations during winter in female adolescents: associations with forearm bone mineral density.
Effects of different dress styles on vitamin D levels in healthy young Jordanian women.
Tryptophan missense mutation in the ligand-binding domain of the vitamin D receptor causes severe resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D.
Poca vitamina D preoccupa i polmoni
Vi � un'associazione fra scarse concentrazioni sieriche di vitamina D ed il rischio di infezioni acute del tratto respiratorio. Recentemente � stato dimostrato che la vitamina D ha un ruolo nel legame fra attivazione recettoriale e risposte antibatteriche. Le differenze nella capacit� di produrre vitamina D potrebbero pertanto contribuire alla suscettibilit� alle infezioni batteriche. In futuro sar� necessario tenere in considerazione gli studi clinici sull'integrazione della vitamina D per accertare se essa migliori l'immunit� nei confronti della infezioni batteriche. La concentrazione di vitamina D risulta maggiore nei soggetti che facevano esercizio prima del servizio militare e minore nei fumatori. (Am J Clin Nutr 2007; 86: 714-7, 2007)
Vitamin D and the regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and innate immunity in colorectal cancer. 2007 and Db=pubmed&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=17867386&ordinalpos=1&itool=vitamin EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum
Vitamin D and autoimmune disease. 2007
Mitochondria, endothelial cell function, and vascular diseases. 2014
When exposed to senescent signals, cellular SIRT1 and FoxO are downregulated, which results in downregulation of the antioxidant MnSOD.
Vitamin D and inflammation
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Mar;103(3-5):563-6. Epub 2006 Dec 23.Click here to read Links
Involvement of the vitamin D receptor in the regulation of NF-kappaB activity in fibroblasts.
Szeto FL, Sun J, Kong J, Duan Y, Liao A, Madara JL, Li YC.
Committee on Molecular Metabolism and Nutrition, Biological Science Division, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637, USA.
We have used mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) derived from VDR and VDR mice to determine whether the nuclear vitamin D receptor (VDR) is directly involved in the regulation of NF-kappaB activation. We found that the basal IkappaBalpha protein level was markedly decreased in VDR MEFs compared to VDR MEFs; however, degradation of IkappaBalpha and its phosphorylation were not altered in VDR cells, neither were the levels of IKKalpha and IKKbeta proteins. Consistently, p65 nuclear translocation was increased in unstimulated VDR cells. The physical interaction between VDR and p65 was absent in VDR MEFs, which may free p65 and increase its activity. Consequently, these alterations combined led to a marked increase in NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. Consistently, induction of IL-6 by TNFalpha or IL-1beta was much more robust in VDR than in VDR cells, indicating that VDR cells are more susceptible to inflammatory stimulation. Therefore, fibroblasts lacking VDR appear to be more pro-inflammatory due to the intrinsic high NF-kappaB activity. The reduction of IkappaBalpha in VDR MEFs may be partially explained by the lack of VDR-mediated stabilization of IkappaBalpha by 1,25(OH)(2)D(3). These data suggest that VDR plays an inhibitory role in the regulation of NF-kappaB activation.
1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits anti-CD40 plus IL-4-mediated IgE production in vitro.
Kaposi sarcoma is a therapeutic target for vitamin D(3) receptor agonist.
Regulation of IL-1 family cytokines IL-1alpha, IL-1 receptor antagonist, and IL-18 by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in primary keratinocytes.
Transcriptional repression of the interleukin-2 gene by vitamin D3: direct inhibition of NFATp/AP-1 complex formation by a nuclear hormone receptor.
1 alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits gamma-interferon synthesis by normal human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 production and vitamin D3 receptor expression are developmentally regulated during differentiation of human monocytes into macrophages.
Vitamin D receptor signaling contributes to susceptibility to infection with Leishmania major. 2007
Una review in italiano abbastanza completa su Le Scienze Dicembdre 2007, pag 96.

Vitamin D, Pit-1, GH, and PRL: possible roles in breast cancer development.
vvvvv
vvvvvvvv
vvvvvvvvvvv